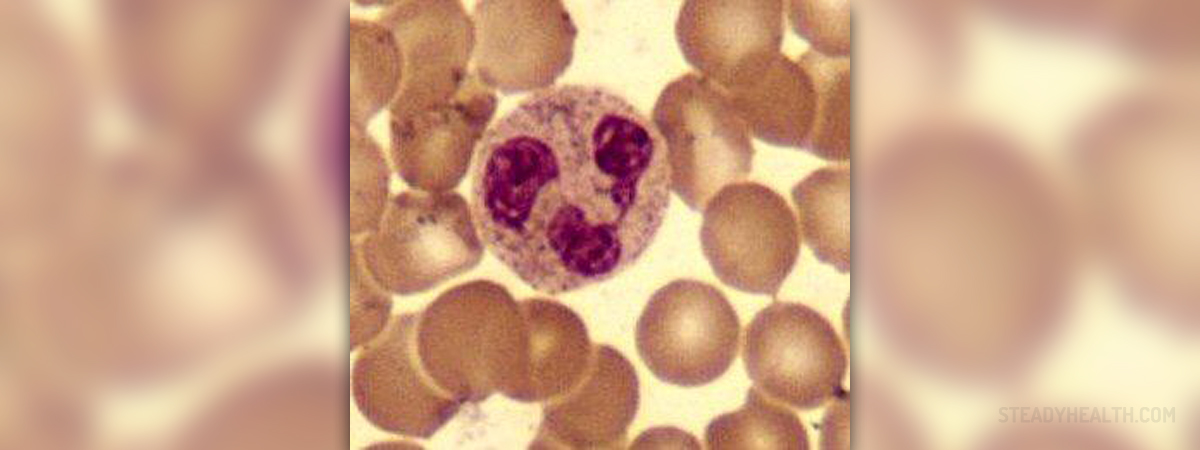
Neutrophils are a type of white blood cells (leukocytes). They belong to a subtype called granulocytes. These cells are a part of the immune system, that are responsible for defense of the body, against many foreign particles and infective agents. Neutrophils are normally produced in the bone marrow. They account for approximately 45-79% of the all white blood cells. Low neutrophil count is medically known as neutropenia and if it occurs it makes a person more susceptible to infections.
Low Neutrophil Count: Causes
Low neutrophil count is, in many cases associated with malfunction of the bone marrow. The bone marrow can be affected with many illnesses such as congenital disorders, cancer, viral infections etc., which does not allow the bone marrow to produce a sufficient number of neutrophils. Furthermore, low neutrophil count may be a consequence of increased damage to these white blood cells. This is typical for some autoimmune illnesses such as systemic lupus erythematosus. And finally, an insufficient number of neutrophils can be a side effect of certain medications.
Presentation of Low Neutrophil Count
People suffering from neutropenia may not show any specific symptoms or signs. The problem is generally related to increased susceptibility to infections. This is why frequent infection may point to the presence of neutropenia. The easiest way to confirm low number of neutrophils is to take samples of blood and have it tested.
Neurtopenia can be classified as mild, moderate and severe. In mild neutropenia there is a minimal risk of infection. In moderate neutropenia the risk of infection is moderate and severe neurtorenia carries increased risk of infection. People suffering from severe neutropenia are very susceptible to infections and the infection is also hard to deal with.
Low Neutrophil Count: Treatment
It is essential for the underlying condition to be determined. This way a patient suffering from low neutrophil count can be treated properly. Infections are treated with antibiotics or antifungal drugs (depending on the infective agent). Furthermore, some patients are administered substances which are able to stimulate the production of leukocytes. Granulocyte transfusions and corticosteroids are two more options. And finally, some patients require intravenous immune globulin.
Apart from medication therapy patients suffering from low neutrophil count should have well-balanced and nutritious diet, plenty of sleep and they are advised to deal with stress.
People suffering from severe neurtopenia are always hospitalized and they are not allowed visits until the number of neutrophils become high enough to protect them against infections.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...