Haemophilia is inherited, genetic blood disorder. Haemophilia is when blood can not clot and it causes excessive bleeding. Blood cells called platelets combine with clotting factors (proteins) and they stick the blood so that bleeding can stop. Persons with haemophilia bleed longer than usual because they do not have enough clotting factors. Usual symptom of this disorder is external bleeding. Also, symptom can be internal bleeding, commonly around muscles or joints. Internal symptoms cause stiffness and pain. Prolonged internal symptoms can cause joints damage.
Haemophilia can have severe, moderate and mild symptoms. There are two types of haemophilia: haemophilia A and haemophilia B. People with first type of haemophilia have problems with some clotting factors while people with second type have problems with other clotting factors. These two types of haemophilia have same symptoms. The most common type is haemophilia A.
Haemophilia can not be cured but genetically engineered clotting factors can help in treatment long-lasting bleeding. There are also some new medications to help in haemophilia treatment. They do not contain human blood cells like older medications so risk of hepatitis C or HIV is reduced.
Symptoms of haemophilia depend on levels of clotting factors.
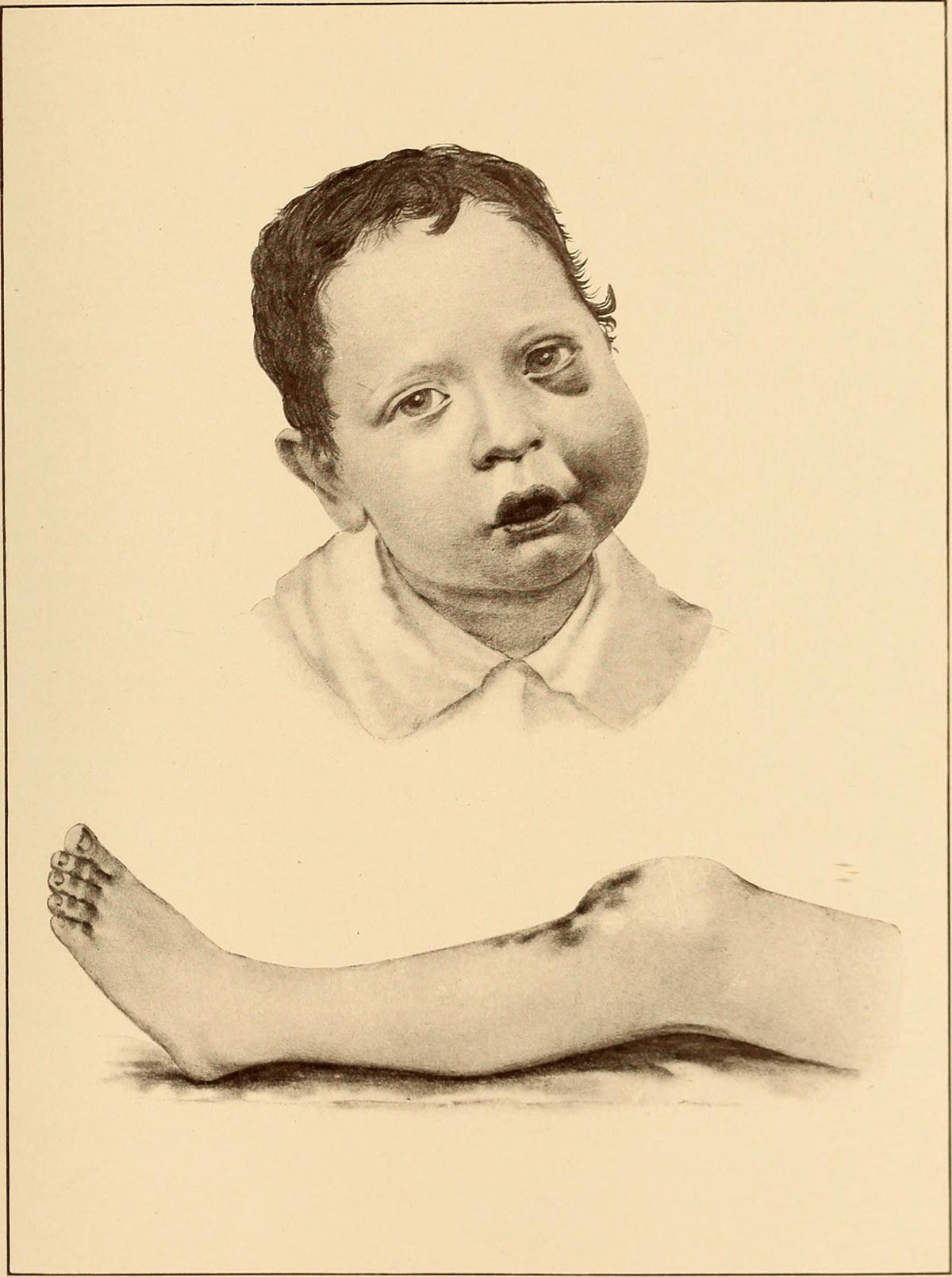
Symptoms can be mild if you have 5 to 30% of normal levels of clotting factors and this condition of mild haemophilia. Symptoms of this haemophilia can occur if you have surgery or dental filling. They break skin and than bleeding occur for prolonged time. Also, children with mild haemophilia can have prolonged bleeding after circumcision. This is removing of foreskin, usually in Jewish and Islamic people. With children who have with mild haemophilia, is possible not to have any symptoms for many years. Children who have 1 to 5% of clotting factors are affected with moderate haemophilia. Their skin bruises very easily. They can have internal bleeding around joints also called joint bleed. Joints that usually get joint bleed are elbow joints, ankle and knee joints. Symptoms of joint bleed are swollen, hot and tender site of bleeding, severe pain in joints and stiffness.
Children with less than 1% of normal levels of clotting factor can have severe haemophilia. Symptoms are frequent and severe joint bleed and spontaneous bleeding. Spontaneous bleeding means that bleeding occurs without reason. The most common spontaneous bleeding are bleeding gums and nosebleeds. The most severe spontaneous bleeding is bleeding inside the skull. In this case is needed emergency medical help. This bleeding is not common and symptoms are: vomiting, double vision, severe headache, loss of balance and coordination, confusion, facial paralysis, stiff neck and slurred speech.








-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)




-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)
Your thoughts on this
Loading...