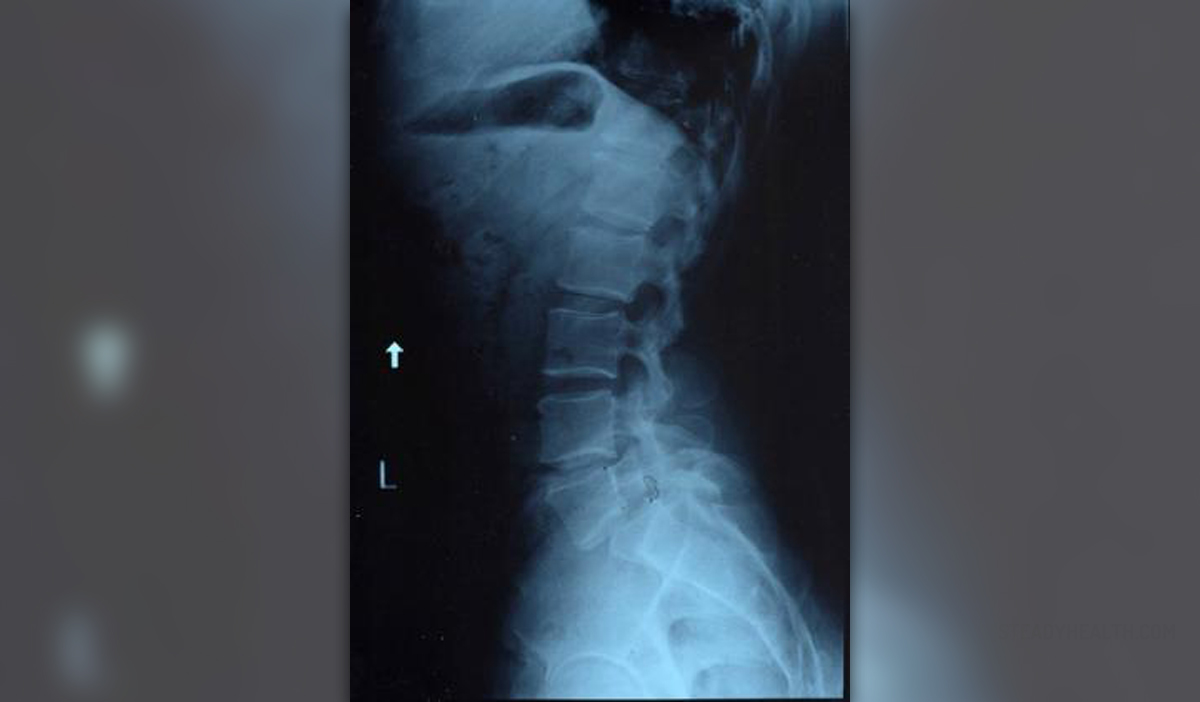
Cervical spondylosis is a degenerative condition affecting the intervertebral disks in the neck. The changes that occur lead to cervical osteoarthritis in the joints which connect cervical vertebras. This condition is common for people older than 55. Its progress continues with age. The disease causes pain, stiffness and muscle spasms. The pain may be located only in the neck or it can radiate towards the shoulders, arms or chest. Tingling and pinprick sensations in the arms may occur. Upper extremities may be weak or numb. Coordination of movements may decrease.
Basically when people age their bones and cartilage deteriorates. This can result in overgrown bones or bones which do not form properly. These changes also known as bone spurs are always present in cervical spondylosis. They can form in other parts of the spine during the aging process. Intravertebral discs degenerate in years as they lose elasticity. This may lead to protrusion of the discs and its herniation. The muscles and ligaments tend to be stiffer in years. All of the previously mentioned point to the fact that cervical spondylosis really is an age related disease.
This is the most common disease of all spinal cord conditions in the elderly population. Sometimes a cervical radiculopathy can develop as a result of the cervical spondylosis. This state is caused by the overgrown bone and bone spurs which compress the cervical nerves. Cervical myelopathy may develop if the spinal canal becomes so narrow that it leads to spinal cord injury.
Symptoms of cervical spondylosis vary so at first they worsen then they decrease in severity but are usually present all the time. The aim of the treatment is reduction of pain so that a person can continue with regular activities and prevention of potential complications such as spinal cord injuries.
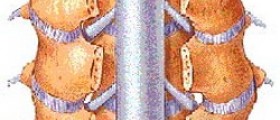
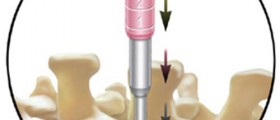
Mild cases are treated with a collar brace. It reduces the neck movements hence decreases the pain and nerve irritation. Pain relievers may be taken but only if prescribed by a doctor. Physical therapy includes certain exercise (regular walk or light activities) which may strengthen the cervical muscles and eventually reduce the pain. If cases are more severe there are two treatments that are surgical and non surgical. The first includes the traction of the neck. This reduces the pressure on the cervical nerves. Modified exercise is recommended. In the case of muscle spasms, relaxants and painkillers are prescribed. Sometimes injections of corticosteroids in the tissue around the disc may be helpful. These medications are also combined with local anesthetics.For all the patients whose pain and additional symptoms cannot be regulated conservatively, a surgery maybe the only option.


-Causes,-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)







Your thoughts on this
Loading...