Vulvodynia- Overview
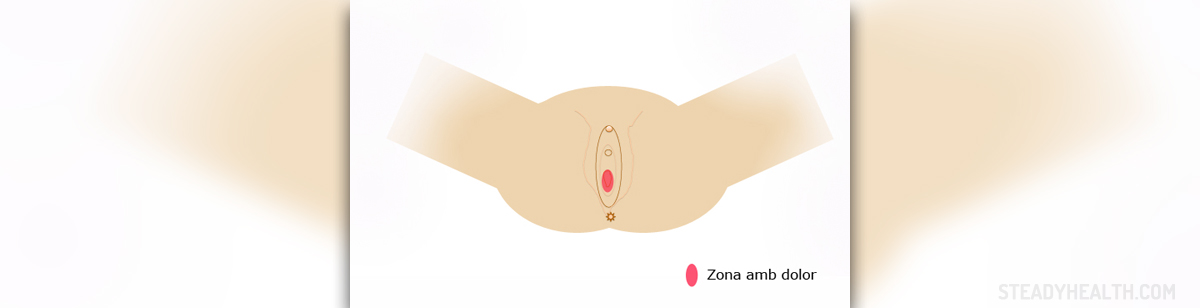
Vulvar discomfort or pain that lasts at least the few months up to a few years can be defined as vulvodynia. Vulvar vestibulitis is a form of vulvodynia featuring with pain only when pressure is applied to the vestibule. The pain typically occurs during intercourse or application of tampons. Vulvodynia might be rather embarrassing and unpleasant condition making it hard for a woman to engage in sexual activity. It also affects women's ability to work and perform everyday duties. It may even affect social interactions.
The leading symptoms include burning and stinging sensations of the vulva. Irritation of the vulva and redness of the skin occur as well. Some women complain about discomfort while others report pain in vulvar area. The pain varies in intensity and precise location. Pain may be induced or occur spontaneously.
The exact cause of vulvodynia has not been identified yet. Doctors believe that several factors may contribute to the disease. They include injury or irritation of vulvar nerves, local hypersensitivity to Candida, allergy to certain irritants, increased levels of oxalate crystals in urine and spasm of pelvic muscles.
Conservative Treatment for Vulvodynia
Unfortunately, there is no specific cure for vulvodynia. The goal of the treatment is to alleviate the symptoms of the disease. Patients may be prescribed tricyclic antidepressants, anticonvulsants, interferon or topical corticosteroids. They may also be advised to change their diets. Antidepressants are basically prescribed to women who are suffering from depression caused by vulvodynia.
In some women biofeedback program, which includes enhancement of individual's ability to control involuntary nervous system, may be of significant help. It can teach a woman to relax pelvic muscles as much as possible, prevent spasms and reduce the pain caused by vulvodynia.
Surgery for Vulvodynia
Surgery is the last option for women whose symptoms cannot be successfully eliminated or at least successfully alleviated by conservative treatment. Surgery is not performed in women who suffer from pain in the entire vulva. Surgical procedure includes removal of major and minor vestibular glands. Some women require a skin graft to the vestibular area. So the bottom line is that the sensitive areas around the vaginal vestibule are resected and the healthy skin is pulled over the excised area. The surgery is successful in 60 to 75% of patients and provides with painless intercourse. The recovery time lasts approximately 6 to 8 weeks.
Some doctors perform laser surgery even though this treatment modality has not been proved to be effective. It may even happen that symptoms of the disease worsen after laser surgery. Today this type of surgery is not recommended in case of vulvodynia.
Pudendal nerve decompression is another surgical procedure which includes cutting of the pudendal nerve. This is performed in case that the pain originates from the pudendal nerve.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...