What is a parotidectomy?
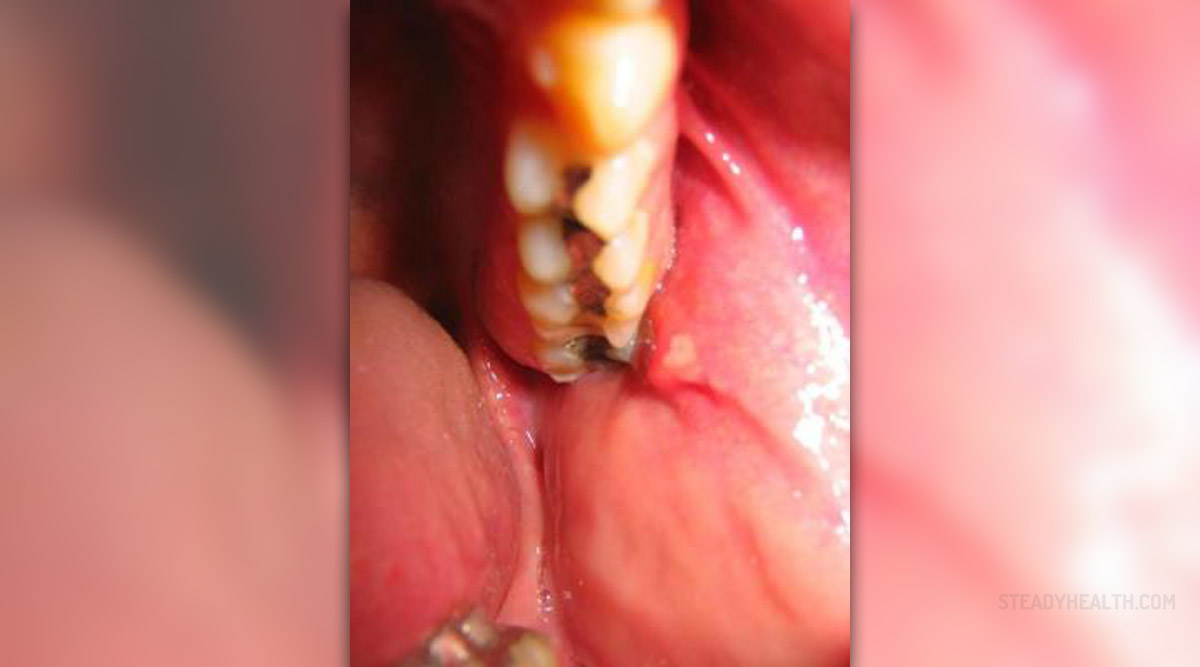
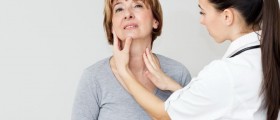
The parotid gland is the largest salivary gland producing saliva. Other salivary glands include the submandibular and sublingual glands. The parotid gland is settled between the jaw and the ear, in the parotid space, looking like a pyramid. This gland may become infected, swollen, or develop tumors, which can be both benign or cancerous. Patients may feel a tumor of parotid gland as a bump between the jaw and their ear.
Parotid removal surgery, medically known as parotidectomy, is a surgical removal of the parotid gland.
Usually, a parotidectomy will be recommended if the parotid gland is affected by a tumor, if it is infected or obstructing the flow of saliva. Some traumas to the head might also lead to parotid injuries that lead to a parotidectomy. The parotid gland may be removed if it gets in the way of a deep tumor or other structure in the brain, needed to be operated.
Symptoms of Parotid Infections
An infected parotid gland may cause wide variety of symptoms that can range from a headache, fever, muscle and joint pains, and swelling of the face, to a palpatable bump — patients can feel the lump under the chin or on the cheek.
In case of parotid tumors, the tumor grows slowly and this is very painful for the patient. Enlarged salivary glands, a dry mouth, sores and infections, sialoliths and tooth decay may indicate a parotid tumor.
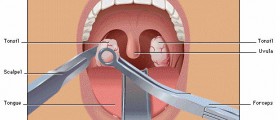
A parotidectomy may be superficial, removing only the outer, cancerous part of the gland. A total parotidectomy is used to remove parotid tumors which affect deep parts of the gland. Sometimes, this type of surgery requires the removal of the facial nerve as well. Possible complications of this operation may be weak facial movements, but a full recovery is usually expected after a couple of months. There is also extracapsular parotidectomy, a minimally invasive surgery that does not affect the facial nerve. Patients must be mobile in two planes, without facial nerve weakness or any previous parotid surgery, to be eligible for this type of surgical removal of a parotid tumor.
Complications of parotidectomy
Parotid removal surgery has all the same risks that any surgical procedure carries. There is the connected to the use of anesthesia, bleeding during and after the surgery, and possible infection. Some of the risks are associated with the specific surgery in question, and these include facial nerve weakness, facial indentation, re-appearance of the tumor, numbness of the ear or face and Frey’s syndrome. Frey’s syndrome is a condition presented as sweating and redness of the cheek, close to the ear.
After the surgery, many patients feel numbness of the ear and earlobes, which should subside over time.
Salivary fistula is a rare complication of parotidectomy, and patients have their saliva drained through a small opening in the surgical cut. This may have to be repaired in a follow-up procedure.
The surgery, especially if the patient is suitable forextracapsular parotidectomy, leaves very little scarring. Risk and possible complications of the surgery are insignificant if compared to the risk of having a tumor or infection in your body.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...