What is cellulitis?
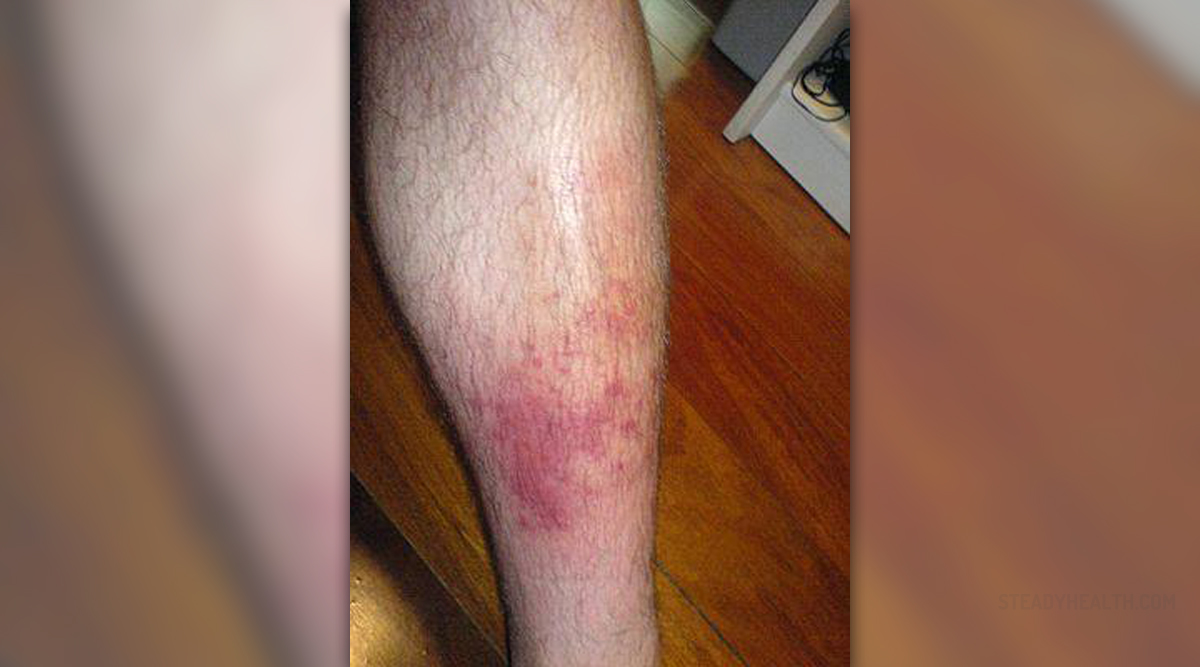
Cellulitis is an acute bacterial infection that affects the layers underneath the skin. It is characterized by redness, pain, warmth and swelling. It can also cause some flu-like symptoms.
This disease usually appears on the parts of the body where the skin is damaged, where there is a cit, abrasion or skin ulcer. Only rarely cellulitis is actually bacteremic, meaning that the bacteria have traveled through the bloodstream.
Certain factors increase the risk of suffering from cellulitis. Those include diabetes and diseases that involve immune system impairment, such as HIV/AIDS. It is not a contagious infection, simply because it is localized in the subcutaneous layers and tissues and the top surface of the skin provides a cover of sorts.
Streptococcus and staphylococcus bacteria, commonly known as strep and staph, are the main and the most common culprits for cellulitis. However, other bacteria can cause it as well- for example, in young children the most common cause is actually Hemophilus influenzae. Cellulitis can also be associated with an animal bite, in which case the bacterium responsible for the infection will most likely be Pasturella multocida.
The exact type of the bacteria that cause cellulitis should be determined through culture tests. Staph infections are mainly treated with penicillin. For other bacteria or for people who are allergic to penicillin, other antibiotics will be used.
In most cases, the infection responds well to antibiotics, especially if they were chosen according to the exact bacterial type. Rarely, cellulitis can cause more serious complications. That usually happens when cellulitis affects the eyes, the face and other sensitive parts of the body.
Signs and symptoms of cellulitis
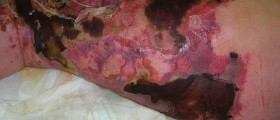
Cellulitis affects the skin structures and tissues underneath the skin. It usually starts as a small, red, swollen and tender area or a feeling of tenderness, burning and pain in and around a skin wound. The area then starts spreading slowly to other parts of the skin. As the red and swollen area starts growing bigger, fever and swollen lymph glands may also set in. The redness may be in form of long and thin streaks or in form of broad areas. Sometimes blisters may form on the affected area.
While impetigo only involves the superficial areas of the skin, cellulitis involves the dermis and other deeper layers of the skin. The involved subcutaneous tissues will become swollen, tender or painful, and they will be warm to touch.
Cellulitis can appear anywhere near a wound, a bite or an ulcer. In adults, it is particularly common on the legs.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...