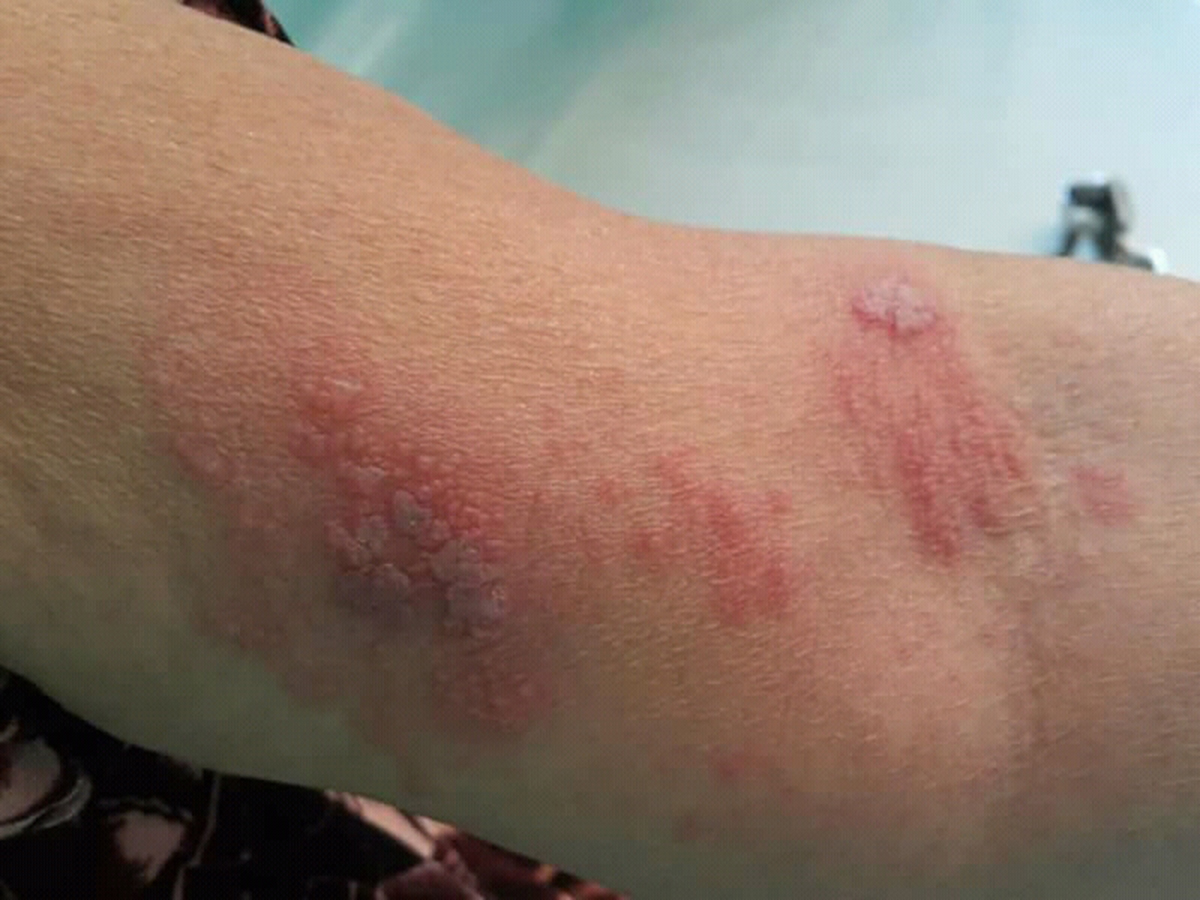
Shingles - Introduction
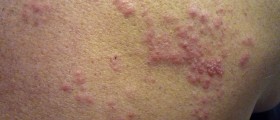
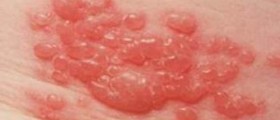
Shingles is a rather the painful skin rash usually accompanied by blisters. It is caused by Varicella-zoster virus, the same one responsible for chickenpox. In people who have had chickenpox Varicella virus never leaves the body. In facts it stays dormant in the nervous tissue. If the immune system of the person becomes weak the virus reactivates and spreads along the nerve fibers affecting the particular area of the skin with characteristic changes. The first symptom of shingles is burning or tingling pain of the affected area. The skin may be numb or itchy. After a few days characteristic skin changes in a form of rash and blisters occur.
Shingles Vaccine
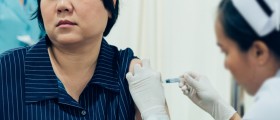
The shingles vaccine is excellent means of avoiding shingles. It is recommended for people over the age of 60 and in people who have had shingles the vaccine may successfully prevent a recurrence of the disease. There have been cases of shingles in children but this disease predominantly affects older people and this is why the vaccine is given to this group of patients.
The vaccine contains a weakened chickenpox virus and once it has been applied it stimulates the immune system to fight shingles. It is effective and reduces the risk of getting shingles. The shingles vaccine may also reduce the length of postherpetic neuralgia, a painful consequence of shingles which usually lasts from days to months or even years after the rash has withdrawn.
The studies confirmed that the shingles vaccine successfully prevents outbreak of the disease in 50% of all cases. Even the risk of postherpetic neuralgia is reduced by about 67%. What needs to be said is that people vaccinated against shingles may develop the disease, but the healing process is much shorter and the risk of complications is minimized. The effects of the vaccine last approximately 4 to 6 years.
People who are supposed to be vaccinated belong to age group 60 and older. Furthermore, the vaccine is also administered in people with compromised immune system such as HIV/AIDS patients and those suffering from cancer.
Risks and Side Effects of Shingles Vaccine
There should be concern in case the person develops rash at the injection site. The problem related to this rash is that it is contagious and may cause chicken pox in small children and pregnant women who have not had the disease. If it occurs the rash must be covered until it heals completely.
The side effects of the vaccine are basically mild and withdraw spontaneously requiring no therapeutic interventions. Local reaction to the vaccine is usually in a form of red skin at the injection site. There may be swelling, itching and characteristic rash may occur. There have also been cases of headache, cold, fever and flu like symptoms after vaccination. In rather rare cases patients have experienced exacerbation of asthma and heart diseases.








Your thoughts on this
Loading...