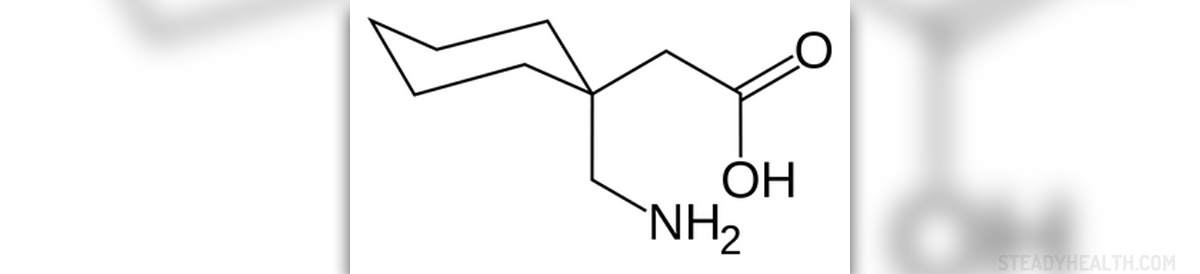
The most common side effects are: sleepiness, dizziness, headache, tiredness and ataxia. General side effects frequently includes asthenia, malaise and facial edema, and cases of generalized edema, weight loss and chill. Sometimes, gabapentin causes vertigo, reflex problems, anxiety, hallucinations, paranoia, euphoria or psychosis, and provoke suicide attempts. It could affect your libido, increasing or decreasing it, and be the reason of brain tumors, cerebellar (part of the brain) disfunction, nystagmus, depression or even status epilepticus. Psychiatric problems are rare, there were some isolated cases of aggressive behavior and hypomania. Gabapentin is often reported to cause anorexia, gingivitis and flatulence, and in some cases gum bleeding, gastroenteritis, hemorrhoids or blood in the stool.
When using gabapentin, patients experienced hear loss, ear infection, earache, increased sensitivity to noise, some of them had perforated ear drum and others reported labyrinthitis and odd smell. Gabapentin may affect your eyes, causing vision problems, cataract, conjunctivitis, photophobia, eye bleeding or twitching, dry eyes or ptosis (drooping of the upper eyelid). Purpura is one of the frequent blood side effects of gabapentin. Other hematologic issues includes anemia, thrombocytopenia or lymphadenopathy. Patients using carbamazepine and gabapentin have experienced decreased in white blood cells.
When using this medication, possible effect might be hypertension. Tachycardia, hypotension, palpitation, murmur or angina pectoris are rare side effects. Gabapentin patients might develop some dermatologic problems, such as hair loss, hirsuitism, seborrhea, dry skin, eczema, sweating and herpes simplex. Skin necrosis, papules or discoloration, psoriasis, herpes zoster or dark pigmentation of the skin are rare side effects. Genitourinary problems are present at some patients. They include urinary retention or incontinence, blood in urine, changes in urination frequency, menstrual and sexual problems, and sometimes breast cancer. Endocrine changes connected to the use of gabapentin are rare. Cases of thyroid, testicle or ovarian problems, and Cushing-like appearance were reported.
Pneumonia is often connected with gabapentin patients. Other respiratory problems that might appear are apnea, epistaxis, laryngitis, dyspnea, mucositis, hyperventilation, nasal obstruction, snoring, bronchospasm, and hypoventilation and lung edema. Gabapentin is rarely affecting kidneys or liver. There are no oncological stydies on people using gabapentin. Male rats using this medication have developed pancreas carcinoma.
Gabapentin patients might suffer from withdrawal effects, if the medication is suddenly stopped. Withdrawal symptoms are present at 2% of the patients and include nausea, vomiting, dizziness, sleepiness, tiredness and ataxia. There were some cases of delirium tremens upon gabapentin withdrawal.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...