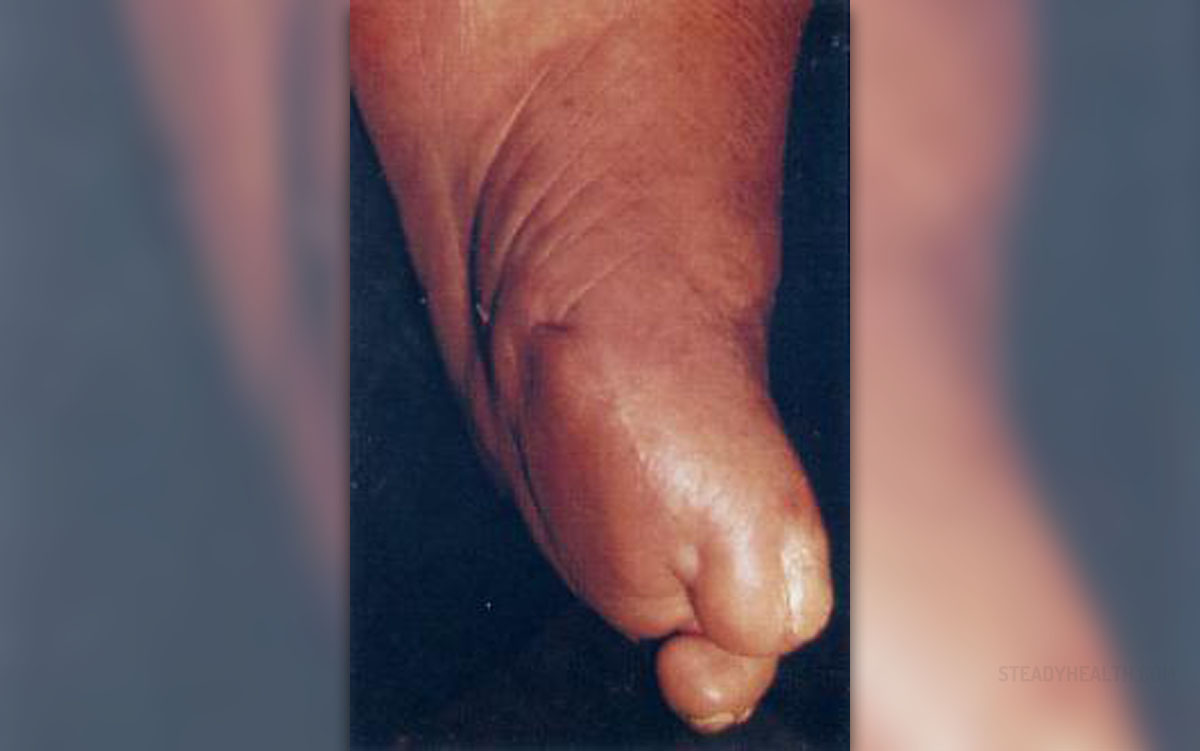
Gangrene is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition. It is actually a complication of necrosis and decay of body tissues. The condition develops under specific circumstances and is usually induced by infection (Clostridium perfigens), injury, thrombosis or ischemia. It also affects people suffering from chronic problems with blood circulation (diabetes mellitus, long-term heavy smokers etc.).
Gangrene always develops if there is crucially insufficient blood supply. It predominantly occurs in the lower extremities. The proper treatment for gangrene is revascularization of the affected organ or body part. Since not all the tissue can be saved necrotic tissue is removed with specific surgical procedures. In severe cases surgical debridement and amputation of the affected body part are performed.
There are several types of gangrene, dry gangrene, wet gangrene and gas gangrene.
Dry Gangrene
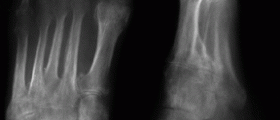
Dry gangrene most commonly affects the distal parts of the limb and occurs due to ischemia. The blood simply cannot reach terminal parts of the limb and this eventually results in necrosis. In majority of cases dry gangrene develops as a consequence of severe atherosclerosis and in this case it affects toes and feet of elderly people. People suffering from many medical conditions which feature with impaired peripheral blood flow are at higher risk of dry gangrene. The tissue affected by dry gangrene is shrunken, dry and dark black. The black color originates from hemoglobin released during hemolysis of red blood cells. Patients suffering from dry gangrene complain about a dull aching sensation of cold in the affected area.
Wet Gangrene
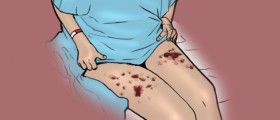
Wet gangrene develops in moist tissues and organs (oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, lungs, cervix etc). A typical example of wet gangrene is a pressure ulcer. In wet gangrene the tissue is infected by saprogenic bacteria. Wet gangrene usually progresses rapidly due to blockage of the nearby blood vessels. Congestion and inappropriate supply of the affected tissue with oxygen allows bacteria to multiply uncontrollably and cause serious damage. The bacteria may also enter the blood stream and cause septicemia. Wet gangrene features with soft, edematous and putrid tissue.
Gas Gangrene
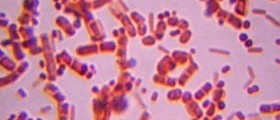
Gas gangrene is caused by Clostridium bacteria hence it is also known as Clostirdial myonecrosis. Gas gangrene features with myonecrosis, production of gas and in advanced stages sepsis. Septic shock may be fatal. Gas gangrene develops as a consequence of wound contamination with Clostridium perfigens. The bacteria multiply and release exotoxins responsible for necrosis of the affected tissue, gas production and sepsis. This type of gangrene progresses rapidly and must be considered a medical emergency and treated promptly.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...