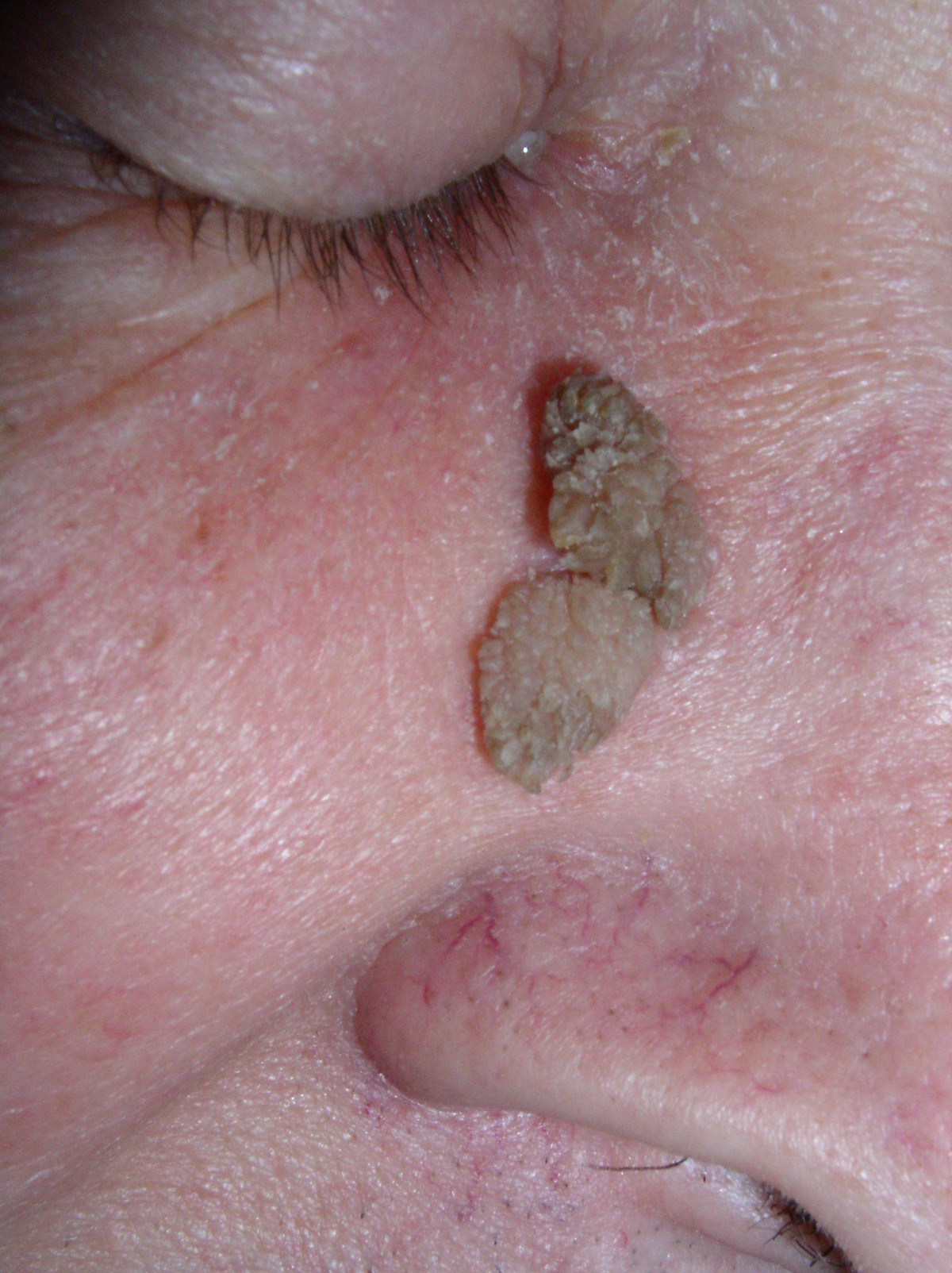
What is Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Seborrheic dermatitis is often a chronic disease that occurs in parts of the skin where there are large sebaceous glands - in the middle of the face, behind the ears and usually on the forehead and scalp. These parts are characterized by oily skin, dandruff and redness. It is more common in men and occurs in infants and people between 30 and 60 year of life.Causes
The exact cause of seborrhea is unknown. It can be associated with hormonal changes in children and usually disappears at puberty.Also, the cause may be fungi malassezia that is normally found on the skin in small number. But if it is multiplied, it causes problems on the skin.
Seborrhoic changes often occur as a consequence of neurological problems such as Parkinson's disease or epilepsy. The reason, why these diseases are connected, is not known.
Periods with intense symptoms - redness and signs of inflammation, fatty and scurfy areas (hairy part of head, the central part of the face, ears, chest and groin) alternate with periods when symptoms are withdrawn.
Treatment
Method of seborrheic dermatitis treatment depends on the place which is affected and the age of the patient. There is no cure for this skin disease. Treatment is only directed to relieving symptoms and reducing their incidence. Given that the disease tends to return, treatment can be time-consuming and requires much patience.The treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in adults uses different drugs that are applied to skin lesions, and in some severe cases, treatment consists of taking the drug orally.
Treatment includes antibiotics when infection is present in skin lesions. Tetracyclines are used in most cases. Some drugs with sebosuppressive action (to prevent increased secretion of sebum) are used in severe cases. These are oral contraceptives or synthetic antiandrogens.
Drugs such as corticosteroids or isotretionin can lead to improvements in severe cases.
The local therapy includes selenium sulfide, agents containing sulfur, salicylic acid, and tar shampoos. Lotions or creams containing corticosteroids are also used.
A good effect is also achieved by using antifungal preparations, because fungi Pityrosporum ovale has the important role in the occurrence of disease.
If there is a bacterial infection it is necessary to use antibiotics locally as a supplementation. It is also necessary to use antimycotic preparations in the case of Candida infection.
Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp is usually treated by shampoos containing salicylic acid. Some of them are prescribed as preparations based on selenium sulfide or zinc. These shampoos can be used 2 times a week. They should be rubbed on the head and let it to act for 5 minutes in order to have effect. If the shampoo does not help, a doctor may prescribe a steroid lotion which is used twice daily in addition to shampoo.
Seborrheic regions of the body which are not covered by hair are treated by moderately stimulating lotions.
Scalp seborrhea in infants and small children are treated with much milder preparations than in adults. Treatment should start with children’s mild shampoos, soft brushing baby's head with a soft brush and a gentle massage baby's scalp with warm olive oil. If this does not help, a doctor may prescribe a shampoo which may contain small amounts of tar or 2% ketoconazole.
General measures of treating seborrheic dermatitis include adequate diet which prohibits oversweet food, spices, hot drinks and alcohol. Recreation, sleep and body hygiene are recommended. Pronounced systemic factors such as infection, emotional stress, unbalanced diet and constipation should be treated.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...