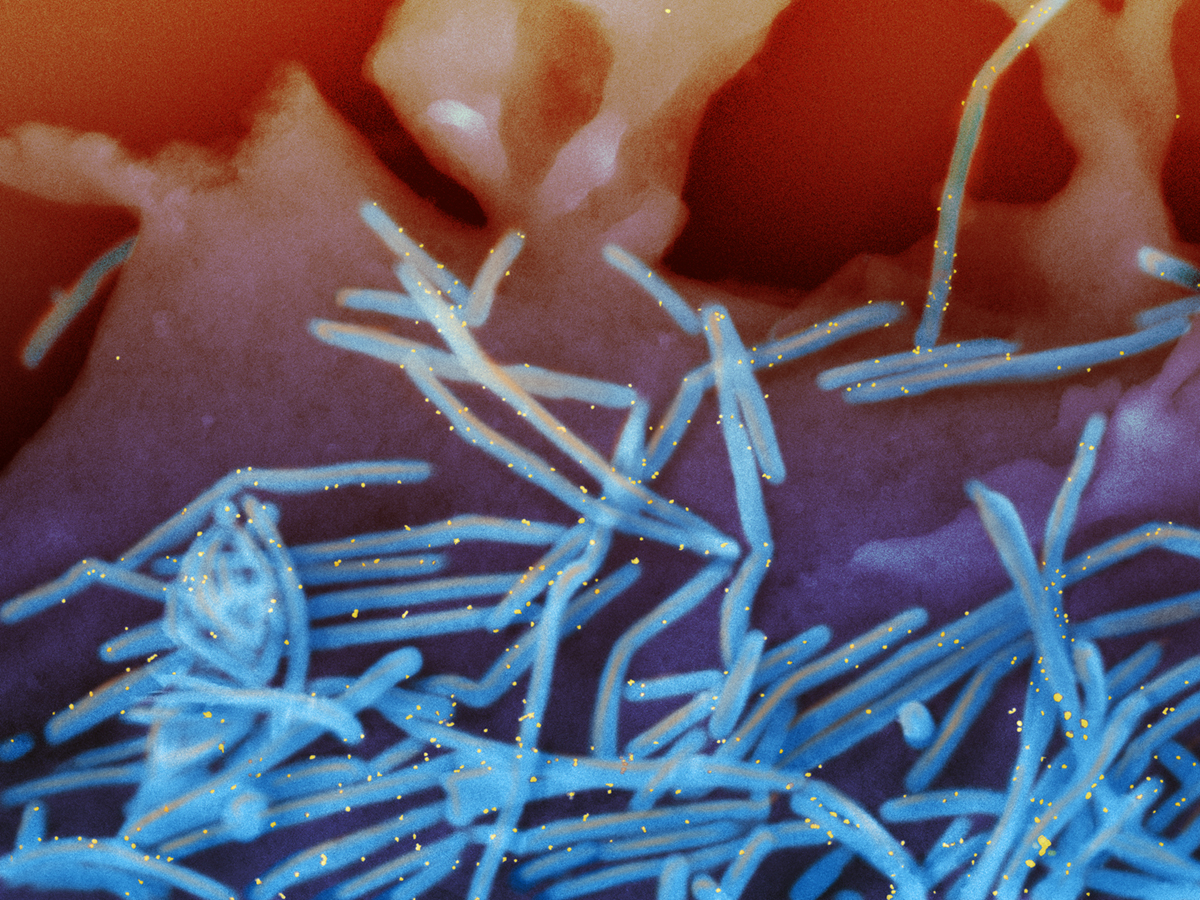
Respiratory syncytial virus – RSV
Respiratory syncytial virus is a virus responsible for the occurrence of the lungs and respiratory tract infections. This virus is very common and many children up to their 2 years of life are infected by it. Adults can be also infected by respiratory syncytial virus. The main cause of this condition is the presence of the mentioned virus in the body. It should be known that this condition is contagious and can be easily spread from person to person. The most favorable seasons for this virus and its spreading are autumn and winter.
Symptoms of respiratory syncytial virus – RSV
In the majority of cases, when the elderly people, adults and healthy children are infected by this virus, the symptoms are not very serious and usually are very similar to those symptoms of a common cold. In such cases, medical treatment is not necessary, and home treatment is enough. Usually, the first symptoms appear four or six days after the virus entered the body. The most common symptoms of mild respiratory syncytial virus are dry cough, sore throat and congested or runny nose. Many people that are infected by this virus may also experience mild fever or headache, as well as restlessness, uneasiness, and malaise or discomfort.
On the other side, severe respiratory syncytial virus usually occurs in premature babies and infants that are already suffering with some other diseases. Furthermore, it can also appear in adults that are suffering from heart or lung diseases. In these cases, untreated respiratory syncytial virus can cause certain complications such as pneumonia or bronchiolitis. It is the medical term for the inflammation of the bronchioles or small airway passages that enter the lungs. The most common symptoms of severe respiratory syncytial virus are severe cough, high fever and wheezing. Furthermore, the person with this virus may complain also of rapid breathing or difficulty breathing. Cyanosis is also a symptom of severe RSV, and it is a medical term for the bluish color of the skin that occurs because of the oxygen insufficiency.
Typically, the children are more affected. Their breathing is shallow, short and rapid, accompanied by coughing. Moreover, the loss of appetite appears and the child shows the signs of irritation and lethargy. The infected person recovers approximately within eight to fifteen days. The recovery time is much longer when severe respiratory syncytial virus is in question, and in most cases, it requires hospitalization because it can even be fatal for premature born babies or for the elderly people with lung or heart problems.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...