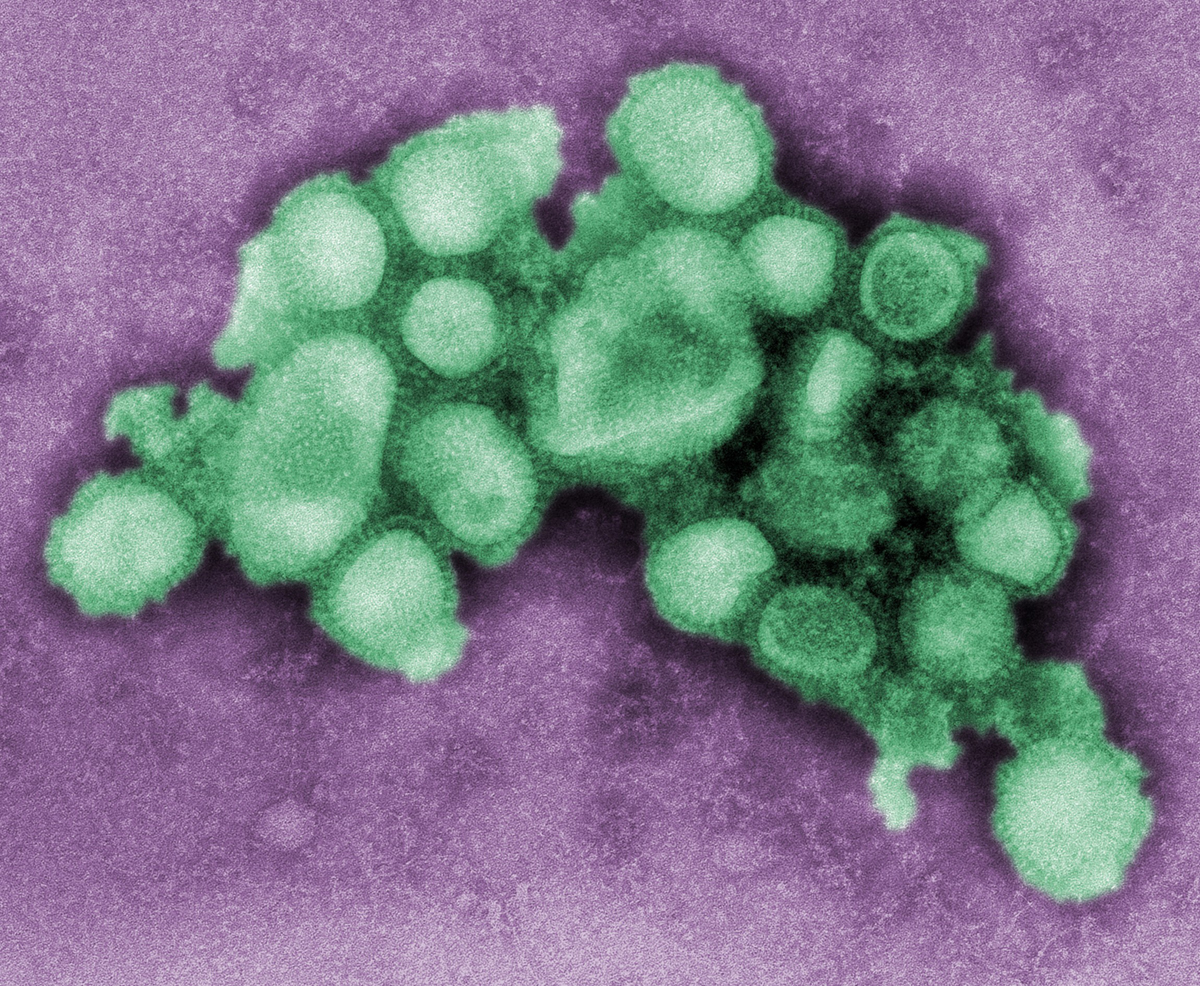
Swine flu is a common name for an influenza A H1N1 virus. This is a new type of flu virus. Since it is relatively new many people have not actually developed the immunity to the virus. This is why the swine flu virus can cause a pandemia. Swine flu pandemia occurred in the year 2009/2010. Today the virus is a part of a seasonal flu vaccine.
Swine Flu Risk Groups
When it comes to seasonal flu the virus predominantly affects young children, people suffering from chronic medical conditions and elderly people. These people are more susceptible to flu comparing to other groups. On the other hand, people who are at a higher risk when it comes to swine flu include pregnant women, children younger than 2 years of age, people suffering from chronic illnesses (e.g. asthma, cardiovascular disease, diabetes etc.) and immunocompromised patients.
Symptoms of Swine Flu
Symptoms and signs of swine flu generally resemble symptoms and signs of seasonal flu. This is why patients suffering from swine flu commonly complain about fever (which is usually high), chills, cough, runny/stuffy nose, sore throat, headache and body aches. Some patients do not suffer from increased body temperature but all of them feel extreme fatigue. In some cases there may be vomiting and diarrhea. The infection can progress and one may develop secondary infection such as pneumonia and respiratory failure.
In some cases the infection can progress and a person can develop more serious symptoms and signs that require urgent medical help and in some cases hospitalization. For example, it is not a good sign if breathing becomes fast and if one develops breathing difficulties. Furthermore, bluish or gray skin discoloration (cyanosis) points to the lack of oxygen and severe breathing difficulties. Patients who do not take plenty of fluids and those suffering from frequent vomiting may get dehydrated. If there is a problem in communication with the patient, he/she requires an immediate medical attention.
How Is the Infection Transmitted?
Swine flu is transmitted via direct contact with respiratory secretions of the infected person. Namely, droplets that contain viral particles are easily spread by coughing, sneezing or even during conversation if people are in close contact. The person becomes infective one day prior the onset of the infection. He/she continues being infective for approximately seven more days. Apart from a direct spread of the virus the infection can be transmitted via contaminated surfaces such as doorknobs, drinking glasses or kitchen counter. Still, since the virus simply cannot survive for a longer period of time without a host, it can only be spread this way if one touches such surfaces soon after they have been contaminated by an infected person.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...