
Overview of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is the most widespread type of tumor in the US with over 3 million instances of the disease diagnosed in more than 2 million individuals every year. Moreover, there are more annual occurrences of skin cancer than those of the breast, lung, colon, and prostate combined. Statistically, one in every five individuals living in the US will develop some form of skin cancer during their life. Almost all cases of non melanoma skin cancers are related to the overexposure to the sun.
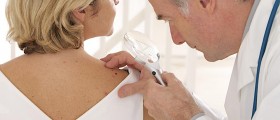
Non-Melanoma (Basal or Squamous Cell) Skin Cancer
The basal cell cancer is the most prevalent form of skin cancer affecting almost 3 million Americans every year. Aside from causing deformation, basal cell cancer can result in death of the patient. The second most prevalent form of skin cancer is the squamous cell tumor, with a little less than a million cases reported annually. Squamous cell cancer causes over 2000 deaths in America every year. In the past few decades the incidences of basal and squamous skin cancer have increased numerous times.
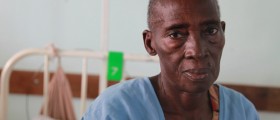
Melanoma Skin Cancer
Melanoma is a serious form of cancer killing one individual every sixty minutes, while in the course of a lifetime one in 50 people will be diagnosed with melanoma. In case the melanoma is caught in its early stages the survival rate is 99 percent, but it is still the most common type of cancer among young individuals. Unless diagnosed early, the survival rate drops drastically to only 15 percent. Similarly to non melanoma cancer, most cases of melanoma are due to overexposure to the ultraviolet rays. In addition, contrary to many of the widespread cancers, the instances of melanoma are more frequent now than they have been in the past couple of decades. A little over half of diagnosed cases of melanoma are obtrusive, while less than 10 percent end in death. Melanoma is not the most common type of skin cancer, but it is the cause of the most skin cancer death cases. On the upside, the death rate of melanoma decreased substantially in the past 50 years. When it comes to women under 40, the only type of cancer that is more likely to be developed is the cancer of the breast. The incidences of melanoma among women have been increasing in the past 2 decades. Those individuals who survive a case of melanoma are almost 10 times more likely to be diagnosed with a new form of skin cancer than those who have never had such a diagnosis. Older men are more likely to be affected and killed by melanoma than older women, while Caucasians are more prone to skin cancer than other races. Individuals who are exposed to ultraviolet rays the most and therefore are at the highest risk for developing a form of skin cancer are men over the age of 40. Men over the age of 60 are also at a higher risk the majority of the population. Before the age of 40 women are more susceptible to developing melanoma than men, but this trend is reversed for individuals in the 50th decade of life and up. Melanoma is not as prevalent in children as it is in adults, although the diagnosed instances have been on the rise in the past 30 years. As skin cancers are developed due to accumulation of adverse effects, melanoma is far more likely to attack children older than 10 years than those who are younger. Girls are more susceptible to melanoma than boys. When it comes to the racial background of patients affected by melanoma, Asians and Africa Americans are more likely than Caucasians to be diagnosed at a later stage. Although instances of melanoma are rare in non Caucasians it is equally fatal for everyone. In non Caucasians, skin cancer usually develops on palms and soles.
Risk Factors for Skin Cancer
The risk factors for developing any type of skin cancer are numerous, and start in childhood. Any kind of severe sun burns in childhood can double the risk for developing skin cancer later in life. Further, overexposure to ultraviolet rays, whether indoor or outdoor, increases the possibility one will develop skin cancer. Indoor tanning beds are considered to be just as dangerous as plutonium by the International Agency for Research on Cancer. The exposure to ultraviolet rays in indoor tanning beds is more than 10 times higher than when tanning outdoors. Out of the 30 million individuals who tan indoors in America more than 2 million are teenagers. Young women are far more likely to use the services of indoor tanning than any other group. Indoor tanning increases the risk for melanoma by more than 70 percent, while the users are twice as likely to develop basal, and squamous cell cancers than the general population.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...