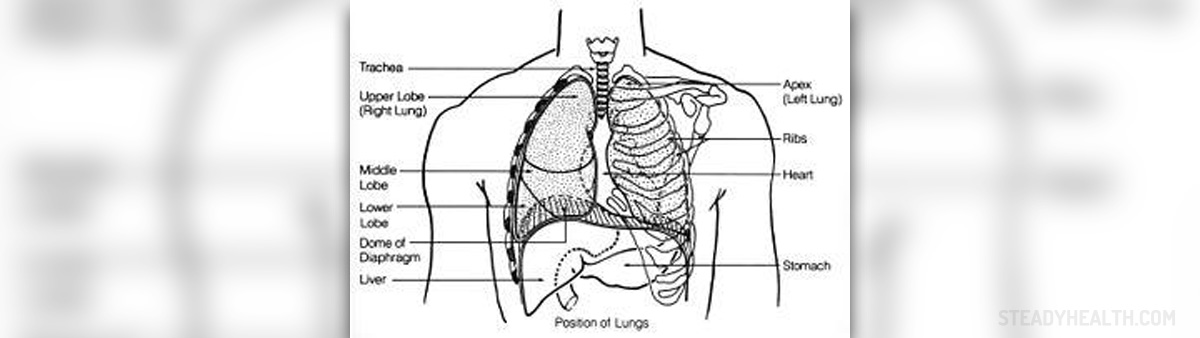
There are actually two different types of respiratory infections. Respiratory infection may affect the lower or the upper respiratory tract. The lower respiratory infection affect the lower parts of the respiratory tract such as trachea or the lungs, while the upper respiratory infection affects the upper parts of the respiratory tract such as the pharynx, nose or sinus.
Upper respiratory infection
The upper respiratory tract is common triggered due to various different types of pathogens such as bacteria or viruses. Once the pathogen attacks the respiratory system, the first symptoms of the infections usually start kicking in after up to 3 days. Upper respiratory infections can be caused by touching the mouth or nose with infected hands, sharing infected food or even by hand shaking. It is an interesting fact that regular smokers are much more prone to lower respiratory infections than to upper respiratory infections. One of the most common causes of lower respiratory infections is a medical condition known as pneumonia.
Symptoms of Respiratory Infections
In order to determine the proper treatment method, one needs to determine whether he or she is suffering from lower respiratory infections or upper respiratory infections. The symptoms of these different types of infections are very similar but there are still certain differences, so it can at times be very difficult to determine which type of infection the person suffers from. Symptoms of the lower respiratory infections are much more severe and serious than the symptoms commonly associated with upper respiratory infections. The most common symptom of the lower respiratory infection is cough. Other common symptoms of lower respiratory infections may include fatigue, high fever, body pain, a tight feeling in the chest, sore throat, blocked nose, sinusitis, headaches, wheezing, shortness of breath and coughing up of blood stained phlegm. The most common symptoms of upper respiratory infections include runny nose, stuffy nose, facial pressure, muscle ache, sneezing, sore throat and headaches. Other symptoms of upper respiratory infection may include laryngitis, bronchitis, sinusitis, common cold, ear infections, coughing up blood, excess mucus and nasal congestions.
Treatment of Respiratory Infections
In most cases, both upper respiratory infections and lower respiratory infections heal on their own without the need for any specific treatment method. There are still some cases of respiratory infections which may be a little bit more severe, so they require a visit to the doctor in order to determine a proper treatment method. These infections are much easier to prevent than to treat.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...