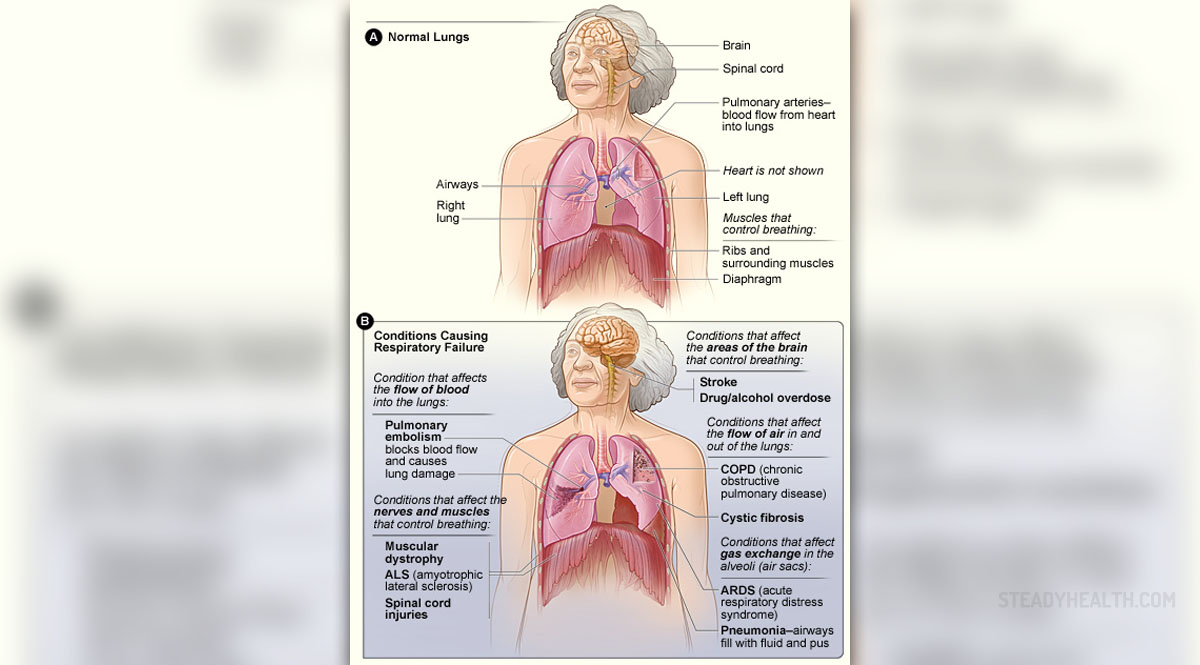
Respiratory failure is a medical term that refers to an inadequate gas exchange by the respiratory system. Since there is an improper gas exchange arterial oxygen and carbon dioxide levels are not in a normal range. The level of oxygen drops while the level of carbon dioxide elevates.
A drop of oxygen in the blood is known as hypoxemia. On the other hand, elevation of carbon dioxide is medically known as hypercapnia. The normal values of PaO2 are over 80mmHg and PaCO2 must be below 45mmHg. Types of Respiratory Failure
There are two types of respiratory failure.
In type I there is hypoxemia without hypercapnia. This type of respiratory failure develops as a consequence of a ventilation/ perfusion mismatch. It is common for patients suffering from parenchymal disease, diseases of vasculature and shunts, pulmonary embolism, interstitial lung disease such as ARDS, pneumonia and emphysema.
In type II respiratory failure there is a decrease of PaO2 and increase of PaCO2. There is also a decrease of pH. This type of respiratory failure occurs due to an increased airway resistance and is common in the fatigued patients (with reduced breathing effort) and emphysema.
What are Causes of Respiratory Failure?
Almost every condition that affect the lungs may eventually cause respiratory failure. For example pulmonary dysfunctions associated with respiratory failure include asthma, emphysema, COPD, pneumonia, pneumotorax, pulmonary contusion, hemothorax, ARDS and cystic fibrosis.
It can also affect patients suffering from cardiac dysfunction such as pulmonary edema, cerebrovascular accident, arrhythmia, congestive heart failure and a valve pathology. And finally, there are several more conditions that may cause respiratory failure including fatigue associated with prolonged tachypnea, intoxication with certain drugs, neurological illnesses and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Symptoms of Respiratory Failure
Low oxygen levels in the blood are responsible for shortness of breath and since there is no sufficient amount of oxygen and there is too much carbon dioxide the skin becomes bluish. This is known as cyanosis and it first affects periphery of the body such as fingertips and lips. Patients are confused and sleepy. Insufficient supply of the brain with oxygen eventually leads to drowsiness and there may also be abnormal heart rhythms.
Treatment for Respiratory Failure
Patients suffering from respiratory failure are hospitalized and treated at intensive care unit. They are initially administered oxygen. The dose of administered oxygen is precisely determined. The underlying condition requires a proper treatment. For instance, in case of bacterial pneumonia patients are treated with antibiotics, patients suffering from asthma require bronchodilatators etc. In case breathing is not restored it is assisted with a mechanical ventilator.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...