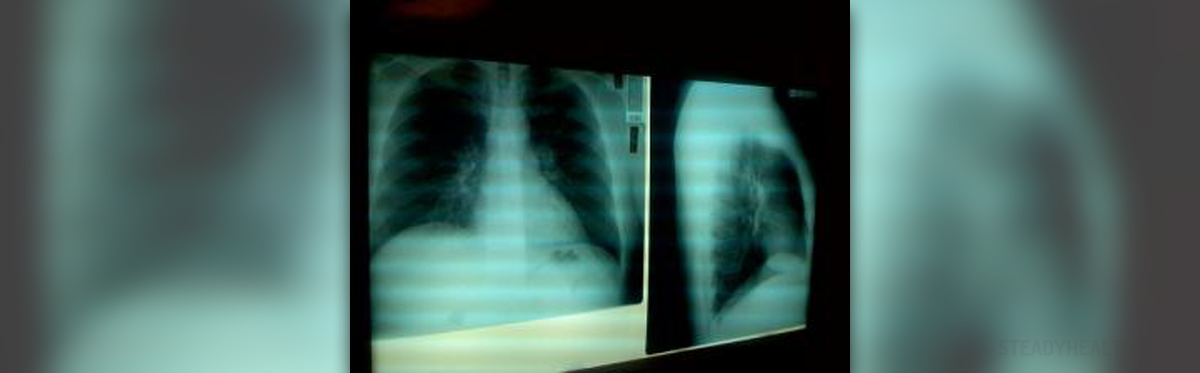
Pneumonia: A Very Serious Condition
The respiratory disease pneumonia can be a very dangerous infection caused by bacteria, fungi, parasites, viruses, or an injury to the lungs. In pneumonia, the air sacs essential to breathing, called the alveoli, become inflamed. They fill with pus or with fluid, making breathing a serious task and robbing the body of adequate oxygen supply.
The causative agents behind pneumonia can enter the body through breathing (mouth or nose), or through the eyes. Pneumonia can affect one or both sides of the lungs if the person’s body is not capable to defending itself from the pathogens that can lead to an infection.
The symptoms of pneumonia are many and varied, ranging from chest, muscle and abdominal pain, to a high body temperature (fever) and severe coughs, to diarrhea, vomiting and overwhelmingly feeling exhausted.
As far as the treatment for pneumonia goes, it strictly depends on the underlying pathogen that caused pneumonia in the first place.
If the infection is bacterial or mycoplasmal, there are antibiotics that will cure it. However, if the pneumonia resulted from a viral infection, for example COVID-19 pneumonia, there are no medical treatments to cure the pneumonia, and the treatment is focused on symptom management. In this case, it is crucial to give the body time and support to fight the virus.
Bacterial Pneumonia: How Patients Can Speed Their Recovery
Even though bacterial pneumonia is treated with antibiotics, it is very important to note that the infected individual’s conduct while they have pneumonia greatly affects the outcome of the treatment; bacterial pneumonia can keep coming back unless it was successfully fought off the first time. Whenever someone is prescribed antibiotics, it is crucial that they finish the entire course exactly as prescribed, even though it is highly likely that they will begin to feel better within a few days, and perhaps even sooner.
Someone diagnosed with bacterial pneumonia should take care to follow the right steps to get better, even if they are recovering at home instead of being hospitalized. That includes:
- Resting as much as possible, and refraining from any physical activity that makes them feel worse. You can go put your empty tea cup on the kitchen counter if you like, but do not try to clean the house or work out! Stay in bed, if you can.
- Eating a light, doctor recommended diet.
- Drinking plenty of fluids, including hot beverages to help keep your airways open.
- Taking pain and cough medication only as instructed by the doctor. Do not use over the counter remedies without your doctor's green light.
- Making very sure to stay away from smoke and other respiratory irritants.
Only if the person with bacterial pneumonia follows these rules will the antibiotics do their job, and it is crucial to beat the infection the first time it develops for if it comes back it does so on a much greater scale.
How Long Will it Take to Recover from Bacterial Pneumonia?
Recovering from pneumonia is a gradual process. Some people who were diagnosed with bacterial pneumonia will actually feel better within a week. For many, the recovery time takes a few weeks, but if you have bacterial pneumonia, it may also take up to a month to feel OK again. Some of the more prominent symptoms of pneumonia, like a cough and a feeling of fatigue, can follow the person for even longer.
Pathophysiology of Pneumonia
Pneumonia will develop when the alveoli of the lungs get inflamed and start filling up with excess liquid, while they are supposed to be filled with air. Further, pneumonia can result from various types of lower respiratory infections that the body was unable to fight off and in turn they escalated.
Bacterial pneumonia is the most prevalent, with streptococcus pneumoniae being the leading bacteria to cause this type of infection.
In addition, the development of pneumonia occurs in 4 distinctive stages.
- After the initial infection, the first symptoms will occur within one day, in a form of a high body temperature and cough. During the first stage, the clogging of the alveoli takes place while the lungs are being attacked by bacteria.
- During the second stage of pneumonia, the lungs are overwhelmed by debris in the form of epithelial cells, neutrophils and erythrocytes.
- The sign that the pneumonia is in its third stage is the brownish color of the lungs produced by a combination of hemosiderin, decomposition of red blood cells, and fibrinopurulent exudates.
- The fourth or the final stage is the stage in which the negative elements are defeated by the person’s immune system and the optimal functioning processes are returned to normal.
Are Young Children More Vulnerable to Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is the most prevalent cause of death among young children and it is usually produced by a viral or a bacterial infection. The symptoms in young children resemble those of a cold and while pneumonia is not contagious per se, it can be passed on to others through bodily liquids.
As far as the causes of children’s pneumonia go, as is the case with adults, strains of the streptococcus bacteria are most often responsible for the development of the infection. The symptoms are again very similar, including chest pain, diarrhea and exhaustion. When it comes to viruses, those which cause children’s pneumonia are usually strains of the influenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus, rhinovirus, and adenovirus. The symptoms of a viral pneumonia are similar to those of the bacterial except for the severity of the cough, which is stronger when produced by a virus.
Finally, those children who have respiratory problems, are exposed to smoke, and do not have a proper intake of healthy nutrients on a daily basis are more likely to develop pneumonia.
Treatment and Prevention of Pneumonia in Young Children
Pneumonia is routinely diagnosed using x-rays, blood tests and visual examinations, while the course of treatment will depend on the underlying cause of the infection. As is the case with adults, if the children’s pneumonia is caused by bacteria, antibiotics will be prescribed, while the viral infection will heal over time. Similarly, children must lie in bed and eat a proper diet for the duration of the treatment. When it comes to preventing pneumonia in children, a shot called pneumococcal conjugate vaccine is widely administered. However, as preventing any kind of illness goes, good, balanced diet and lots of physical activity coupled by a good overall hygiene of the child go a long way.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...