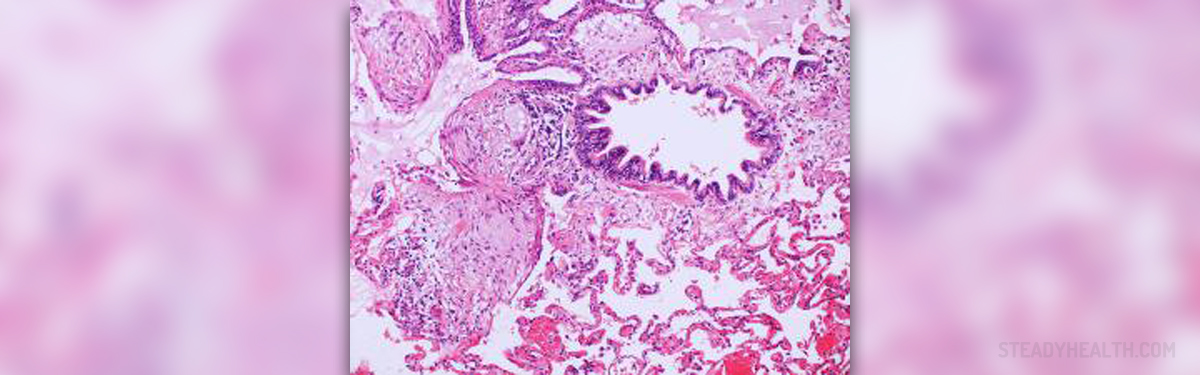
Pneumonia is a lung inflammation, usually caused by infection, which, despite effective antibiotic therapy, results in high mortality (1-5%). Inflammatory exudates are created in the alveoli and interstitium (the space between the alveoli) under the influence of microorganisms multiplication.
Causes
Pneumonia is a relatively common disease, especially, among children below the age of 5 and adults older than 65. The disease has a seasonal character. It is more frequent in the early spring and winter.Factors that encourage development of this inflammation include: smoking, air pollution, cooling the body, the decline in the immunity and chronic diseases, especially diabetes, alcoholism and heart diseases.
Inflammation of previously undamaged lungs (primary pneumonia) may be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa and rickettsia.
Bacterial pneumonia, also called typical, is caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), Straphylococcus aureus, Haemophylus influenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae and other gram-negative bacilli.
Atypical pneumonias are usually caused by influenza viruses A, B and C, adenovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, mycoplasma of pneumonia and rickettsia (Coxiela burneti, Q-fever). The most common causes of pneumonia in children are respiratory viruses, while Mycoplasma of pneumonia is the main reason for lung inflammation in adults.
Pneumonias often occur in previously damaged lungs by edema, myocardial infarction, bronchiectasis or cancer. These are secondary pneumonias, which include pneumonia caused by inhalation of dust, chemicals, food or vomit content.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of pneumonia are fever, chest pain, shortness of breath, cough and expectoration.Typical bacterial pneumonia usually begins abruptly with a fever and high temperature. Cough, accompanied with pussy sputum expectoration is very pronounced. Coughing up bloody sputum or ichor (hemoptysis) and a cold sore on the lip or nose (facial herpes) may also occur. The disease can lead to toxic damage of myocardium which leads to the rapid heart rate and collapse. Severe pneumonia may lead to jaundice (biliary pneumonia).
Atypical pneumonia, which is usually viral, begins gradually, resembling the flu. The temperature increases gradually with the presence of headache, malaise and pain in muscles and joints. Cough occurs after 3-4 days and is usually dry. The diagnosis is made only after radiographic.
Complications
Abscess is a serious and often complication of pneumonia.Also, bronchiectasis, myocarditis, sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome are possible complications of lung inflammation.
The Course and Prognosis
Prognosis depends on the age and immunity of the patient, causes of pneumonia and the presence of chronic illnesses. Young and previously healthy people are completely cured in 2 weeks. Pneumonia can lead to death in children younger than 5 and people older than 65. Particularly difficult course and poor prognosis of pneumonia is in diabetics, asthmatics, smokers and alcoholics.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...