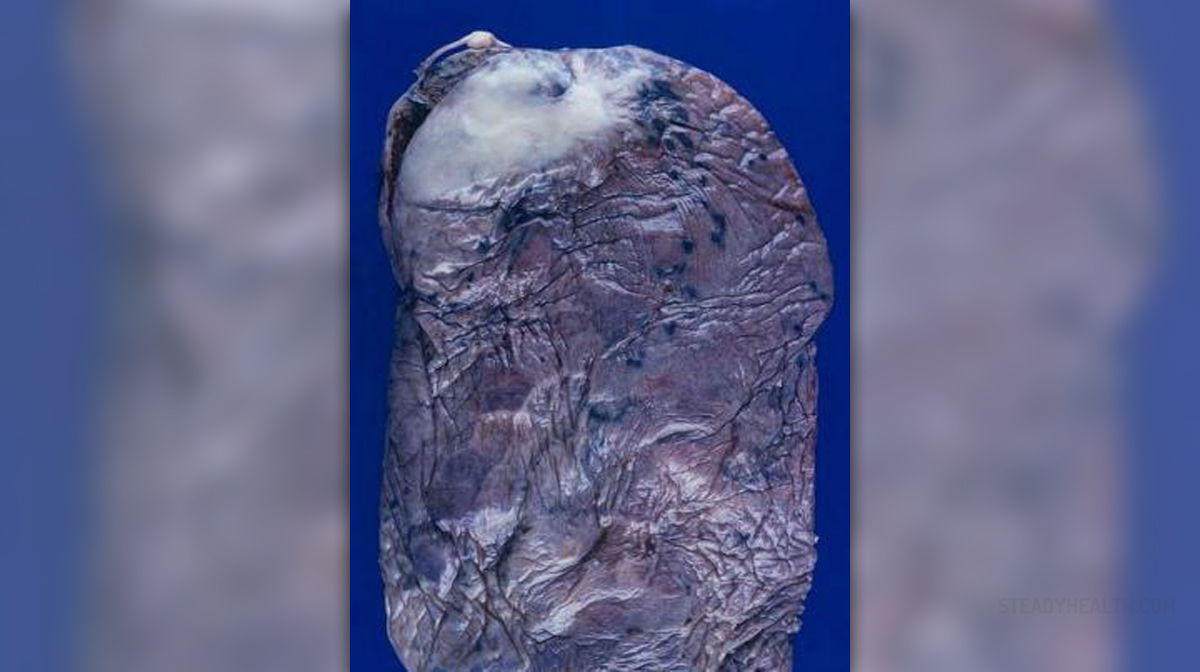
Pulmonary fibrosis is an illness of the pulmonary interstitial space and it can be caused by numerous factors. Essentially, this condition is a sort of inflammation localized in the wall of the alveoli, which is the smallest respiratory unit. It gradually decreases; while the left out space is filled with fiber tissue that does not have the same function as healthy alveoli. This means that when some areas in the lungs get affected by that fiber tissue, lungs simply cannot perform their function as before, which of course, creates obstacles for normal breathing and is, unfortunately, the main cause of tragic end in this condition.
Causes
Factors that lead to this inflammation process are alveoli damaged by some chemicals (inhalation of mercury, high concentration of oxygen etc.), some medicaments, weak immune response thanks to some other condition, several illnesses (collagen and vascular illnesses, systematic lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, ancylosing spondylitis, amyloidosis), radiation, asbestoses.
This condition usually happens at the age of 50, and one of the first symptoms is dyspnea (hard breathing during physical strain), which is minimal in the beginning but later on, it becomes much more serious and it starts happening without any physical activity done. This leads to the increased breathing speed, which happens at the slightest physical exertion. Cyanosis, characterized by blue color of mucosa layers of the lips and surrounding area, happens also with the patient being physically active, and as the condition progresses, this happens while patient is not doing anything. Other symptoms are weight loss, painful joints, anorexia, etc. Radiological examination of lungs and examination of lung function are enough for establishing a diagnosis, while bronchoscope biopsy is used for confirming the presence of this condition in the organism or the absence.
Medicaments
The only medicament that stabilizes this illness and slows down the progress of this illness is corticosteroids. In the early stages of fibrosis, good results can be made, but when the condition progresses, even corticosteroids cannot help. Prednisone is usually given to patients, 1 mg per kilo of body weight, once a day for 8 or even 12 weeks. When the condition regresses, the amount of the medication given may be reduced. In any case, if the condition progresses for long enough, another medication is administrated and that is cyclo phosphamid. In terminal phase of this condition, several methods of symptomatic therapy are used (oxygen, diuretics, cardio tonics), but in cases when nothing else works, there is an option of lung transplantation. Prognosis for this condition is not good since pulmonary fibrosis life expectancy is about 7 years if no transplantation is done.








,-Asthma-And-Anxiety_f_280x120.jpg)





Your thoughts on this
Loading...