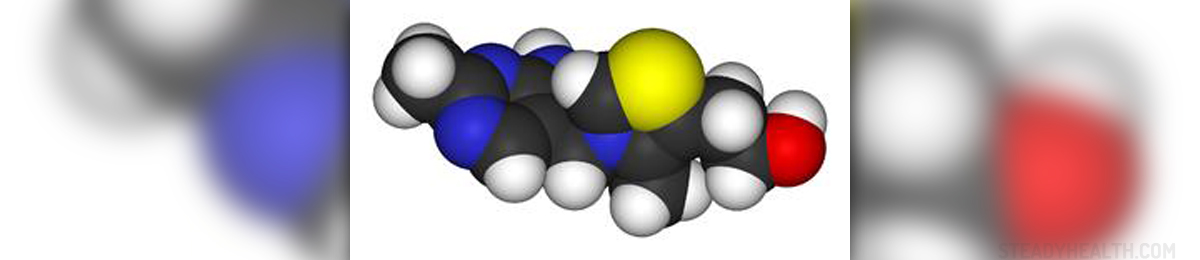
Wernicke's encephalopathy is also known as Korsakoff psychosis and alcoholic encephalopathy. This is a serious brain disorder which leads to complete loss of certain brain functions. The underlying cause of this disorder is lack of thiamine, vitamin B1. Lack of thiamine is closely related to chronic and uncontrollable consumption of alcohol, thus Wernicke's encephalopathy generally affects alcoholics.
Apart from being caused by insufficient amount of thiamine in the body, this disorder may also be associated with direct negative influence of alcohol on the brain and its functions. The disorder is also connected with nonalcoholic conditions such as long-term starvation, excessive vomiting during pregnancy (hyperemesis gravidarum), bariatric surgery, HIV/AIDS and infants who are fed formulas.
Clinical Characteristics of Wernicke's Encephalopathy
Patients suffering from Wernicke's encephalopathy develop a set of symptoms and signs which can be altogether easily recognized with basic symptoms and signs of alcoholism. There is speech difficulty, amnesia, confabulation (the spontaneous narration of the events that have never taken place), double vision, attention deficit, anxiety, disorientation and mental confusion.
Furthermore, such patients may have hypotension, swallowing difficulties and reduced eye movement.Treatment for Wernicke's Encephalopathy
Initially, all patients suffering from Wernicke's encephalopathy require proper prehospital care including stabilization of the airway, ensuring proper amount of oxygen and monitoring and maintaining optimal levels of blood pressure and fluid in the body.
Once patients reach emergency department care they are further treated with suitable medications. For example, in some of them as little as 2 mg of thiamine may be sufficient enough to reverse symptoms of Wernicke's encephalopathy. Still, most of alcoholics actually require much higher doses which can go up to 500 mg given at once or sometimes twice/three times per day. Thiamine is generally administered intravenously. In order to achieve desirable effect doctors use fresh thiamine solutions (old solutions may contain inactive form of the vitamin). The most noticeable results of such therapy include improvement of ataxia and acute confusional state. Doctors further decide which therapy will be needed additionally. Some patients are given intravenous glucose solutions, those suffering from hypomagnesaemia may benefit from parenteral magnesium sulfate etc. Prevention of Wernicke's Encephalopathy
Because it is known that practically all symptoms and signs of Wernicke's encephalopathy develop due to lack of thiamine and that scientist have determined the risk groups which are prone to this disorder, it is clear what preventive measures can be applied. Namely, it is essential to have a healthy diet rich in all the essential nutrients, vitamins and minerals. This way thiamine is obtained in sufficient amounts. Prevention of alcoholism is a perfect way of preventing lack of thiamine and subsequent problems.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...