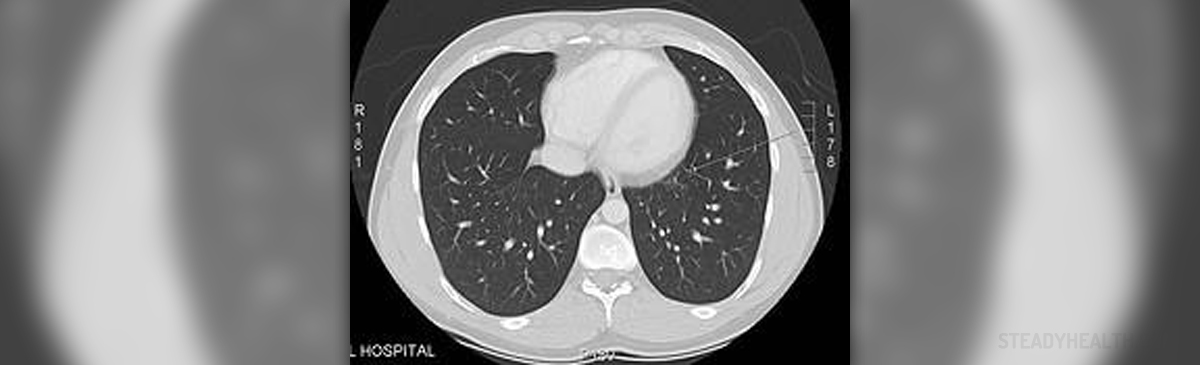
Respiratory disease is the term for a group of conditions affecting the organs involved in breathing. Some of these conditions are asthma, respiratory infections, bronchitis, COPD and lung cancer. Respiratory disease is a common cause of death worldwide. Therefore it is important to take measures to reduce the risk of these illnesses. In the following paragraphs we will deal with prevention of respiratory disease. Diet and Respiratory Disease
A diet plays a key role in every aspect of health. This also includes respiratory health. All body functions, including breathing require fuel, which is obtained from food. Food along with inhaled oxygen gets converted into energy and carbon dioxide. This process is known as metabolism.
Healthy food plays a vital part of the immune system that protects the body against infections and diseases. Thereby, with a healthy diet one can boost his or her immune system and reduce the risk of respiratory infections, which can be very dangerous for individuals suffering from lung problems.
According to some studies, diet during pregnancy has a significant impact on respiratory health of newborns and their risk of developing wheezing, allergy and asthma. Unhealthy diet of the mother lowers the baby’s protection against sensitization to allergens thus increasing the chance of asthma.
A diet high in sodium and refined sugar is a major risk factor for many respiratory diseases. On the other hand, fresh vegetables, fruits, whole grains and quality proteins such as lean meat, seafood, egg whites and low-dairy products are recommended to improve the health of the respiratory system. Plenty of fluids are important to avoid respiratory infections.
Respiratory Disease and Environment
Air pollution is a very important risk factor for respiratory disease. People already affected by this condition are especially vulnerable to environmental pollutants. Dust, fumes and various harmful gasses and particles are abundant in the air we inhale and irritate the lungs resulting in different respiratory conditions. Sources of these pollutants are power stations, factories and motor vehicles.
Indoor air pollutants are equally significant factor in development of respiratory disease. Common indoor pollutants are carbon monoxide, tobacco smoke, mold, dander and household products.
Contaminants present in indoor and outdoor air are primarily associated with respiratory conditions in children. This is because the lungs of children are immature and they also breathe at faster rate comparing to adults thus ingesting more pollutants.
To prevent development of respiratory disease, a person must eliminate pollutants and keep buildings well ventilated. On the other hand, exposure to outdoor air pollutants is difficult to prevent. But, parents can limit their children’s outdoor activities on poor air quality days such as still, sunny days with insufficient wind to disperse pollutants.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...