
Chronic kidney disease represents a slow loss of kidney function which eventually leads to complete inability of the kidneys to excrete excess water and electrolytes as well as waste products from the body.
This medical condition develops as a consequence of many different kidney disorders and is usually gradual. At the end, when kidneys completely stop working, a patient is left with only one option - kidney dialysis.
Causes and Risk Factors for Chronic Kidney Disease
There are many medical conditions which may eventually cause chronic kidney disease. The most common ones are diabetes and hypertension. Obese people, individuals older than 50 years of age, people with a family history of kidney disease as well as smokers are also potential candidates for chronic kidney disease.
Many times the problem is closely related to condition that directly attacks the kidney and all its structures. This is reported in case of diabetes, hypertension, nephritis (inflammation of kidneys)and hereditary kidney diseases (e.g. polycystic kidney disease). Scarring of the organ or the ureters is associated with backflow of urine and also triggers chronic kidney infection.
Hypertension is a systemic disease which affects many different organs. Kidneys are very susceptible to increased blood pressure. Hypertension is blamed for damage to blood vessel throughout the body. Damage to arteries supplying the kidneys with blood in such case is a main reason why kidneys are further damaged.
A person is also possible to end up with chronic kidney disease if he/she is taking drugs such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen regularly, for a long period of time. These medications are known to cause analgesic nephropathy and associated kidney failure.
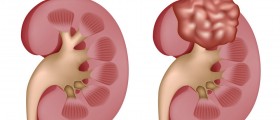
Apart from the mentioned, there are several more diseases associated with chronic kidney disease and these include HIV, sickle cell disease, amyloidosis, kidney stones and some cancers. Heroin abuse is also considered a potential trigger for this medical condition.
Chronic Kidney Disease Prevention
In the majority of cases the condition simply cannot be prevented. Sometimes is, however, possible to protect the kidneys from damage and even slow the progression of the disease once it occurs. This is achieved with treatment and control of the underlying conditions.
Kidney disease may advance significantly until the first symptoms occur. This is the reason why individuals at risk are supposed to undergo screening tests. Screening tests are also recommended for people suffering from diabetes, hypertension and high cholesterol in blood.
Finally, by avoiding long-term use of analgesic drugs (NSAIDs in particular) one will successfully prevent analgesic nephropathy and associated kidney failure.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...