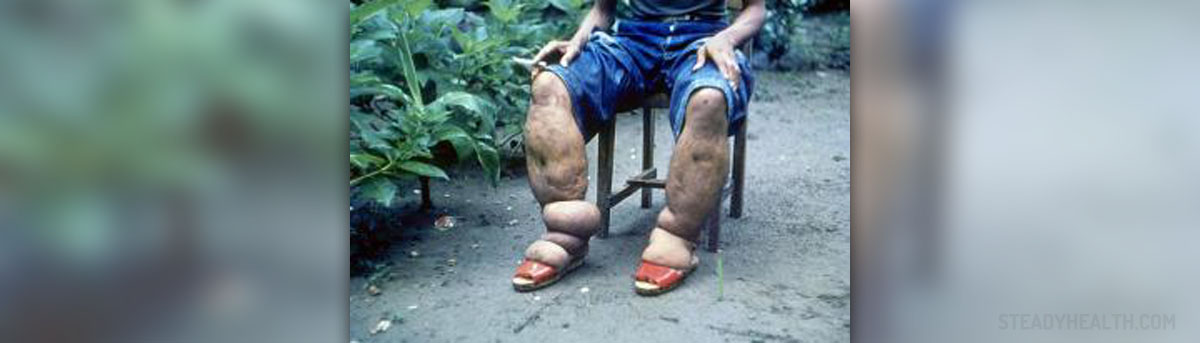
What is Elephantiasis?
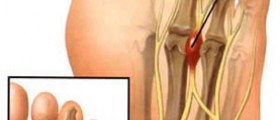
Elephantiasis is the disease which causes abnormal swellingand enlargement of some parts of the human body. Obstruction of the lymphaticvessels is the primary cause of this disease which leads to the swelling of theskin and certain tissues under the skin. The disease usually affects breasts,limbs, lower trunk or genitals and besides the enlargement elephantiasis alsocauses thickening of the skin on these areas of the body.
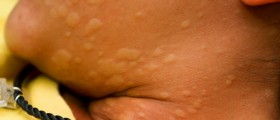
People suffering from elephantiasis may have no symptoms forseveral years or no symptoms at all. However, that is not always the case. Infectionand damage to the lymphatic system may cause swelling, ulcerations and thickeningof the skin of elephantiasis patients. One part of the body’s reaction is alsoresponse of human immune system to parasite invading the body. Patients mayalso experience some pain and fever.
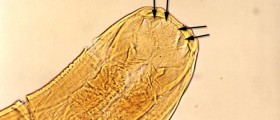
Depending on the cause of the disease there are: lymphatic filariasis(caused by parasites) and non-filarial elephantiasis (podonicosis, caused bylong term exposure to some irritants). Parasitic worms such as: Brugia malayi,Brugia timori and Wuchereria bancrofti are possible causes of lymphatic filariasis.People normally get infected after the bite of the female mosquito and then theworms spread to the lymphatic system. Exposure to alkali metals (sodium orpotassium from the soil) and some other irritants are the cause on non-filarial elephantiasis.
Treatment Methods for Elephantiasis
Success of elephantiasis treatment mainly depends on theearly diagnosis and urgent medical assistance. Damage caused to the tissue is permanent,but the symptoms can be managed.
Medications are able to kill parasites and larvae causingelephantiasis, so these are primary means of treatment for parasitic type ofelephantiasis. There are several drugs which can be used for the therapy, anddoctors usually choose albendazole or diethylcarbamazine. In sub-SaharanAfrica, treatment includes combination of albendazole and ivermectrin. Albendazoleand diethylcarbamazine are able to kill microfilariae and adult worms, whileivermectrin is not so effective for adult parasites.
These drugs are known to cause certain adverse effects,including: fever, headaches and muscle pains, as well as some allergicreactions. Allergies are considered to be provoked by the chemicals remainedafter the destruction of the worms in the body.
Regular cleaning of the affected area and doxycycline treatmentare also beneficial for the patients suffering from parasitic form of elephantiasis.
Non-filarial elephantiasis is treated with elastic bandagesand by wearing shoes, to avoid further exposure to irritants. Management ofthis disease should also include regular cleaning with water and some soap. In certaincases, especially if elephantiasis affects scrotum, surgical intervention may besolution for reduction of this disease.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...