
Seizures, also known as convulsions, represent jerky movements of the body (the entire body or some of its parts) due to abnormal brain activity. They can be easily classified into partial seizures and generalized seizures. There are different body's reactions which occur during seizures some of which are muscle spasm, muscle contractions, loss of consciousness and strange sensations. This medical issue affects people of all ages.
Causes of Partial Seizures in Children
Causes of seizures in infants and older children generally differ. For instance, in infants major triggers for seizures are birth trauma, metabolic imbalances or chemical changes in the body. Fever, different infections, brain tumors as well as congenital disorders are several more conditions associated with seizures in infants and small children.
In adolescents, on the other hand, apart from some underlying medical conditions seizures may occur due to drug and alcohol addiction and intoxication and injury to the head. Types of Partial Seizures in Children
Partial seizures in children can be further classified into simple partial seizures and complex partial seizures.
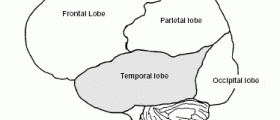
Partial simple seizures usually originate from the occipital lobe. Because this part of the brain contains centers for vision such children commonly experience different visual disturbances. In them even muscle of different parts of the body can get affected. The attack does not last longer than a minute and there is no loss of consciousness.
Partial complex seizures originate from the temporary lobe in majority of cases. This part of the brain is in charge with emotions and some memory functions. This is why abnormal electrical activity in the temporal lobe leads to continuous lip smacking, screaming, laughing, crying, gagging or running. A child may even lose consciousness. These seizures never last longer than 2-3 minutes. Sleepiness and exhaustion are common feelings a child has to deal with after the attack. Partial Seizures in Children Diagnosis and Treatment
All patients undergo physical and neurological examination, blood and urine tests, thorough assessment of medical history as well as family history. EEG (electroencephalography) records abnormal electrical activity of the brain and confirms the condition. Additional tests a child may need to undergo include NNIDS, CAT, MRI or PET.
As for treatment, partial seizures in children are basically treated with medications. They bring under control the attack (if it is ongoing) and prevent further recurrence of the disease. If medications fail to provide with desirable results, a child may benefit from additional treatment like ketogenic diet and vagus nerve stimulation (VNS).











-In-Infants-And-Older-Children_f_280x120.jpg)


Your thoughts on this
Loading...