Introduction
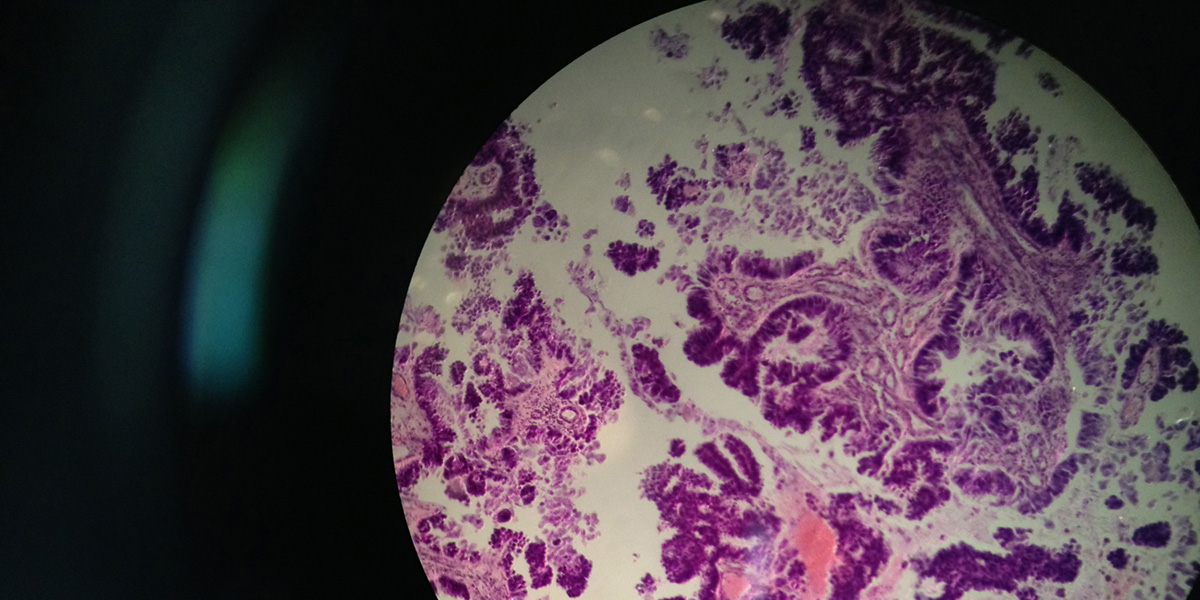
Cancer is often followed by neurological complications. These complications are the second most common reason for hospitalization of cancer patients, just behind the routine chemotherapy. The most common complication is brain metastasis, affecting between 20 and 40 percent of all cancer patients.
Some other complications may be leptomeningeal metastases or epidural spinal cord compression, which is treated as an emergency, by using corticosteroids or surgical decompression. Leptomeningeal metastases may present as a multiple neurological dysfunction.
Metabolic encephalopathy, stroke or hemorrhage is non-cancerous reasons for development of neurological complications in cancer patients. They may develop as a result of chemotherapy side effects, coagulation disorders, direct invasion, etc.
Neurological complications
Initial evaluation of neurologic complications in cancer patients is usually performed by a family physician. The severity and the properties of these complications may vary from patient to patient and from condition to condition. Most common conditions that can produce some of these complications are colon, lung, breast, prostate gland and head cancer and also lymphoma and leukemia.
It is estimated that 15 to 20 percent of all cancer patients will develop symptomatic neurologic complications. The most common symptoms are back pain, headache, changes in personality leg weakness and limb pain. In the near future, rate of those neurologic complications will increase as a result of improved cancer treatments and longer survival rate.
Some new studies indicate that neurologic complications may be even more common than initially claimed. One of those studies, performed in Johns Hopkins Oncology Center, reported that 46 pct. of cancer patients were affected by some neurologic complication in a three-month time and that this condition required medical evaluation or treatment. Other investigation proved that 30 percents of all small cell lung cancer patients had some serious neurologic complication during their illness.
As mentioned before, patients may suffer brain metastases and cerebrovascular complications. As autopsy studies revealed, cerebrovascular lesions were found in 15 pct. of all patients died of cancer. Some reasons for development of cerebrovascular disease may be pressure or invasion on blood vessels by the tumor or coagulation problems related to the initial disease.
Patients may also suffer stroke, and the main suspect for those strokes in cancer patients is nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditic, or in simple terms a sterile vegetation inside one or more heart valves. The reason for neurological disorder in cancer patients may also be a pressure to cranial nerves by a tumor. The "numb chin" syndrome is a result of that kind of pressure. Patients are complaining on a numbness of a lower lip and their chin.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...