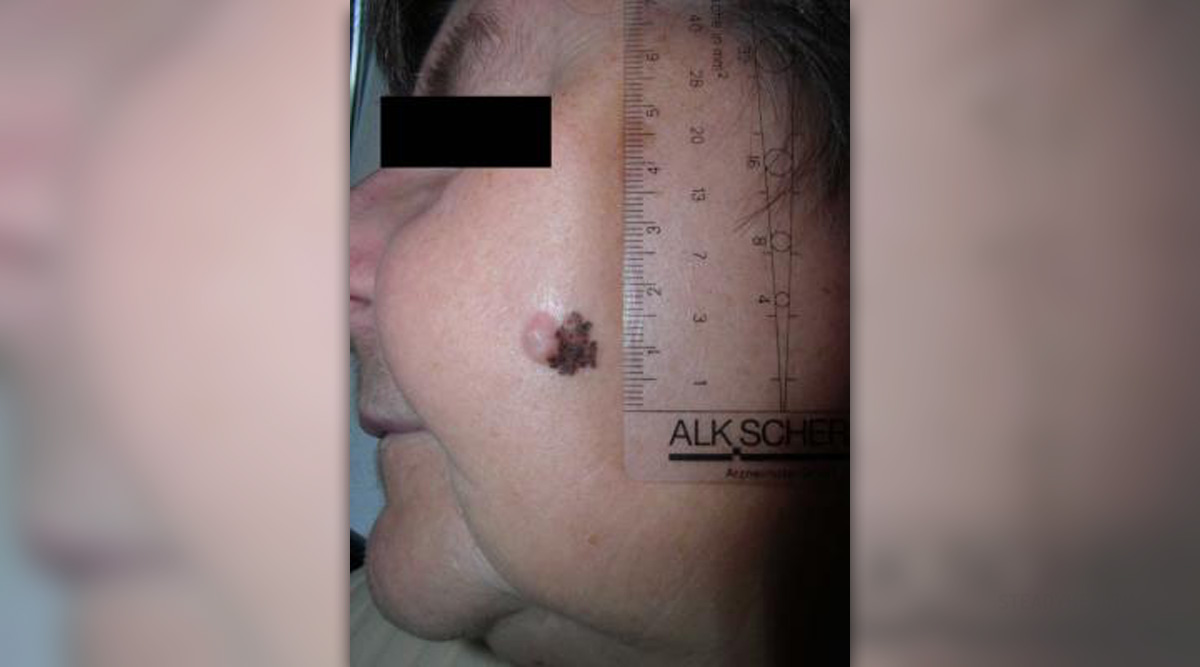
Melanoma is the most severe type of skin cancer. It is a malignant tumor that arises from cells in the skin known as melanocytes, which produce pigment that gives color to the skin. Melanoma can originate in both normal and pigmented skin. Melanoma predominantly affects the skin although it may also occur in the eyes and in the bowels.
In men, melanoma usually develops on the trunk, head and neck whilst in women it is mainly found on the lower legs. Unusual moles may run in families which increases the risk of melanoma. People with this risk factor should regularly perform self-examination for early detection of abnormal changes in moles and symptoms of metastatic melanoma.
Causes of Metastatic MelanomaIt has been estimated that 20% of the malignant melanoma begins in the moles. Exact cause of the cancer is still unknown but several factors increase the risk of development of melanoma.
People who have many moles on their body as well as people with fair skin are more prone to melanoma. Excessive exposure to UV radiation from the sun and severe blistering sunburns particularly in childhood are also factors that increase the risk of melanoma. Family history of melanoma also plays a significant role. People whose family members have been affected by melanoma have a high risk of melanoma.
Symptoms of Metastatic Melanoma
Melanoma usually arises from surface layers of the skin but the cancer often rapidly spreads to the deeper layers of the skin. Then it swiftly spreads by the lymphatic or bloodstream route when it finally reaches distant organs. Metastatic melanoma usually affects the skin, lungs, liver, brain and bones.
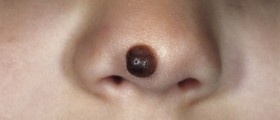
Typically, the first sign of metastatic melanoma is any unusual change in color, shape or size of a mole or other skin growths. Development of new abnormal growth on the skin can also indicate melanoma.
Initially, the growth has flat or slightly raised appearance with color that ranges from black to brown, gray, pink, white or blue.
These cancerous growths are usually asymmetrical, with blurred edges. Sometimes, the tumor may bleed, ooze and itch. Also, the melanoma is usually larger than 6mm in diameter.
In advanced stages of melanoma, skin breakage as well as pain and bleeding from the mole is common. The texture of the mole starts to change which usually results in lumpy and hardened mole. Progressed melanoma also causes swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin and armpit area. Headaches, seizures, chronic cough, recurring fevers and weight loss are common too.
Treatment for Metastatic Melanoma
The treatment for metastatic melanoma is determined by the stage of cancer and organs that are affected. The treatment commonly includes surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy and immunotherapy. In the early stage of the cancer, surgical removal of the melanoma is usually the only treatment.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...