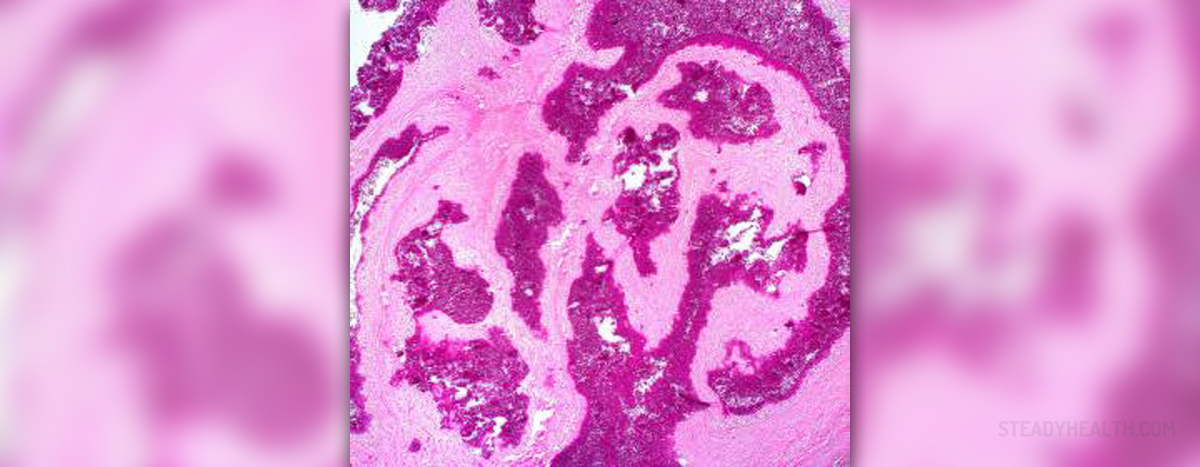
Kidneys are the organs of urinary system for the excretion, located in the upper abdominal cavity. Kidney function assumes maintaining volume of organic liquids content which is achieved by its removing through the urine.
Acute renal failure
It is a condition characterized by decreased urine excretion causing changes in volume and composition of organic liquids. There are prerenal, renal and post-renal causes.In the beginning of the disease the patient has no symptoms that indicate acute renal failure. At this stage comes only to a reduced excretion of urine. After that, patient shows general weakness fatigue and food aversion. Symptoms worsen if there is no intervention on time. The patient loses concentration and becomes very nervous.
In more advanced stage of disease, patient falls into a state of stupor, which is occasionally accompanied with episodes of delirium or cramps. The patient also breathes deeply with periods of complete cessation of breathing. His or her tongue is dry and the muscles tremble involuntarily. Almost regularly after a few days of the occurrence of anuria occurs bleeding or infection. If the treatment not begins at the time the survival rate is 5-10 days from the occurrence of renal insufficiency.
Consequences
One of the acute renal failure consequences is disturbed water balance. When it comes to the impossibility of eliminating the water through the kidneys, then appears hyper hydration. Water intoxication leads to digestive respiratory and heart problems and nervous symptoms.Electrolyte balance disorders leads to permanent consequences. During anuria often appears lack or increase in concentration of potassium, calcium, sodium and phosphorus in the organism which can cause major heart problems.
The kidney is the organ that regulates the acid-base balance. Metabolic acidosis is a common complication of renal insufficiency, causing gastrointestinal and cerebral problems.
Because of acute renal insufficiency comes to retention of nitrogen compounds.
Another important and frequent consequence of acute renal insufficiency is anemia.
And finally there is also another consequence - disorder of coagulation.
Chronic renal failure
Chronic renal failure is the last stage of kidney disease. Irreversibly damage of the nephrons majority causes a chronic inability to eliminate waste through the kidneys. Its causes include numerous pathological conditions and kidney and urinary tract damages. Chronic renal failure is often caused by glomerulonephritides mercury poisoning, kidney infections and congenital anomalies of the kidney. Among the first signs of chronic kidney failure are polyuria and polydipsia. The inability of the remaining nephrons to concentrate urine leads to disorders of electrolyte balance.Start of chronic renal insufficiency is imperceptible. The third of functional kidney tissue is able to process normal amount of substances, so the patient does not feel any symptoms. Only laboratory tests can show decreased glomerular filtration rate and defective ability of concentration.
The amount of urine is higher, and patients must urinate more frequently. As the disease progressively advances appears uremic phase which leads to a series of hematochemical changes. Especially increases urea, creatinine and uric acid which often lead to anemia. Total proteins, calcium and sodium are often decreased, while potassium and phosphorus are increased. Electrolytes are impaired. Because of anemia patient feels a strong general weakness, and tires easily. The patient is pale and often feels nausea, poor appetite and persistent hiccups. Ill person is often depressed, anxious or irritable. Most of these symptoms disappear when patients begin dialysis therapy.
Advanced stage of uremia often leads to pericarditis. This is inflammation which demonstrates in pain behind the sternum and feeling of general weakness.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...