TSH is a short name for thyroid stimulating hormone, also known as thyrotropin. This peptide hormone is produced and released from the thyrotrope cells in the anterior pituitary gland. This gland is situated in the brain, and located near and behind the sinus cavities. The function of thyroid stimulating hormone is to regulate the function of the thyroid gland.
Thyroid gland
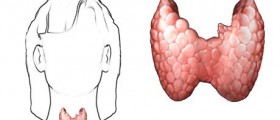
Thyroid gland is one of the largest endocrine glands in the human body, situated in the neck, below the Adam’s apple. The gland has characteristic butterfly shape, and it is very important for normal functioning of the human body. Among many other functions, thyroid gland controls the rate at which body uses energy, makes proteins, and manages how sensitive the body is to other hormones. TSH is involved in secretion of thyroid gland hormones, namely: Triiodothyronine or T3, and Thyroxine or T4.
TSH levels
Levels of thyroid stimulating hormone are dependent on the functioning of a thyroid gland. For example, if the thyroid gland produces less thyroid hormone, the pituitary gland will start to produce more TSH hormones to force the thyroid gland to produce more thyroid hormones. This condition falls in the realm of health disorders, and it is medically known as hypothyroidism.
Similarly, whenever the thyroid gland is overactive and produces excess levels of thyroid hormone, the pituitary gland reacts by lowering the thyroid stimulating hormone levels in order to affect the levels of thyroid hormone. This condition is medically known as hyperthyroidism.
TSH test
TSH levels are normally measured using a common blood test, which reveals problems with the thyroid gland. Testing is commonly performed on newborns to make sure there is no congenital hypothyroidism. Levels of TSH in blood usually vary but for adult persons normal levels are somewhere between 0.4 and 4.5mIU/L. Any measurement below 0.3mIU/L indicates low levels of TSH and requires medical attention.
Low TSH levels
Low levels of TSH manifest in a number of signs and symptoms, which are usually similar to the symptoms of hyperthyroidism. Patient will generally have increased levels of thyroid hormone, which affects the metabolic rate. Therefore, every function in the body will drastically speed up. Patients will usually be very nervous and irritable, they will breathe at an increased rate, and their heartbeats will be very fast-paced. These patients usually have difficulty sleeping, hand tremors, frequent bowel movements, and lighter menstrual periods, in women. Their general adrenaline levels will become increased with results in anxiety symptoms, undesired weight loss and lower levels of serum cholesterol.




-In-Infants-And-Older-Children_f_280x120.jpg)

-During-Pregnancy_f_280x120.jpg)



Your thoughts on this
Loading...