Introduction
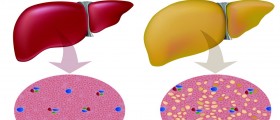
When other methods in the liver treatment fail, the only possible solution is liver transplantation. Technique that is used in most cases is called orthotopic transplantation, and it is a procedure where a liver is replaced with a donated one, and placed where the old one used to be. The downfall of this procedure is that it is one of the most expensive procedures in medicine.
Complications of liver transplantation
Some 60 % of liver transplant patients have some kind of a liver rejection. That is because the body can decode that that liver is not its own and rejects it. When doctors notice liver rejection, medications that can prevent it are given, although there is small number of cases when medications cannot prevent liver rejection and re-transplantation must be done. Most of patients who take immuno-suppressants have episodes with liver rejection during first six months after the transplantation. Obvious signs that can indicate a liver rejection are fatigue and rise in temperature, while other signs require blood tests. It is important to tell your liver transplant coordinator if you experience any of these symptoms.
In the case that rejection is suspected, the patient will undergo a liver biopsy to confirm rejection, which may be mild or serious. If the doctor determines that the body is rejecting the new liver, the present medications will need to be changed. The practice is that the patient who had liver transplantation stays in hospital from 3 to 5 days, and during that time, the right dosage of medicine is obtained, and if the rejection occurs medical staff can react on time. Biopsies are one of the possible methods to determine weather a liver rejection re-appears.
Infections
The medications that are helpful against liver rejection can do harm to the patient's immune system, thus resulting in infections. Virus that appears in most infections is called cytomegalovirus (CMV). Infections of this type in some cases don’t have any symptoms, while in others, the symptoms resemble the ones that occur when we are dealing with flu. The best possible way to stop and prevent the spread of an infection is to wash hands frequently and to suggest the same to anyone who has contacts with a patient.
The lung problem may also occur in liver transplantation. It is because the area where they are operating is near lungs, which is why the patient has to be encouraged to take deep breath and cough. In that way, pneumonia is prevented from developing.
Other possible complications of liver transplantation include kidney problem, biliary problem, primary non-function, hepatic artery thrombosis and portal vein thrombosis. Finally, bleeding occurs as one of the most often complication. In some cases, an operation is required in order to stop bleeding.










_f_280x120.jpg)



Your thoughts on this
Loading...