Introduction
Bone marrow transplantation is a surgical procedure in which an ill person receives the stem cells from the healthy bone marrow of a donor. This is a treatment modality that is used in some malignant diseases which affect the bone marrow. So the patient receives new cells and his/ her sick cells have been completely destroyed prior to the operation. This treatment modality is sometimes the only option for certain cancers such as leukemias, lymphomas, and certain solid tumors. The procedure is performed in case of aplastic anemia as well.
Complications of Bone Marrow Transplantation
There are numerous potential complications after this surgical procedure and they mainly depend on the type of the disease and the type of bone transplant. Some complications are connected to the age of the patient and some depend on his/ her general health. Preparation regimes as well as the discrepancy between the donor's and recipient's tissue are other potential factors of complications.
- The same professional medical interviewer conducted in-depth interviews with 38 subjects (10 men, 28 women; mean age 46.9 years) who had received ablative therapy for bone marrow and/or peripheral blood stem cell transplants.
- Participants were consecutively identified through physician and patient referrals, cancer and BMT patient support groups, and newspaper advertisements. Twenty-eight patients (74%) received autologous stem cell transplants and 10 patients (26%) received allogeneic transplants.
- Participants reported mouth sores, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue as the most troubling side effects of their transplants. Mouth sores were selected as the single most debilitating side effect (42%), followed by nausea and vomiting (13%). Many patients mentioned that mouth sores made it difficult or impossible to eat (n = 23), swallow (n = 21), drink (n = 17), and/or talk (n = 8). Twenty patients reported pain in the mouth, throat, and/or esophagus.
- Two-thirds (66%) of patients reported receiving opioid analgesics, most frequently morphine, to relieve oral pain. For many, opioids caused incapacitating side effects, including hallucinations, a feeling of loss of control and a decrease in mental acuity.
There can be only one problem after the surgery or the patient may develop two or more complications at the same time.
Infections
Infections are rather common complication after bone marrow transplantation. They are caused by the previous immunosuppression. The infections are generally caused by bacteria. In case that infection is caused by viruses or fungi the patient's life is highly jeopardized. The infection leads to possible postponing of engraftment. The patients are therefore isolated after the surgery and are prophylactically administered certain medication.
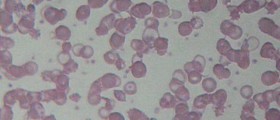
Blood Abnormalities
Anemia, as well as thrombocytopenia, can develop after the transplantation. The cause of these abnormalities is improper functioning of bone marrow. Thrombocytopenia may cause severe hemorrhage especially if it affects gastrointestinal tract or brain.Pain
The pain in transplanted patients is caused by ulcers that form in the oral cavity or gastrointestinal tract.
Excess of Fluid
Excess fluid can cause pneumonia and damage to certain organs such as the liver, kidney and blood vessels.
Respiratory Distress
Respiratory distress is a condition that can be induced by infection (of lungs or other organs), excessive presence of fluid, hemorrhage, or graft-versus-host disease. Respiratory distress is a life-threatening condition.
Organ Damage
Numerous organs can be affected and their structure and function changed. The damage may be temporary or permanent and most commonly affected organs include the liver, kidneys, heart, and so on.
Graft Failure and Graft-Versus-Host-Disease
Graft failure can occur due to infection. Sometimes even the recurrence of the disease leads to graft failure. There may not be enough stem cells from the donor for successful engraftment. Graft-versus-host-disease is severe consequence and is actually a reaction of the patient's body to the foreign tissue (transplant).













Your thoughts on this
Loading...