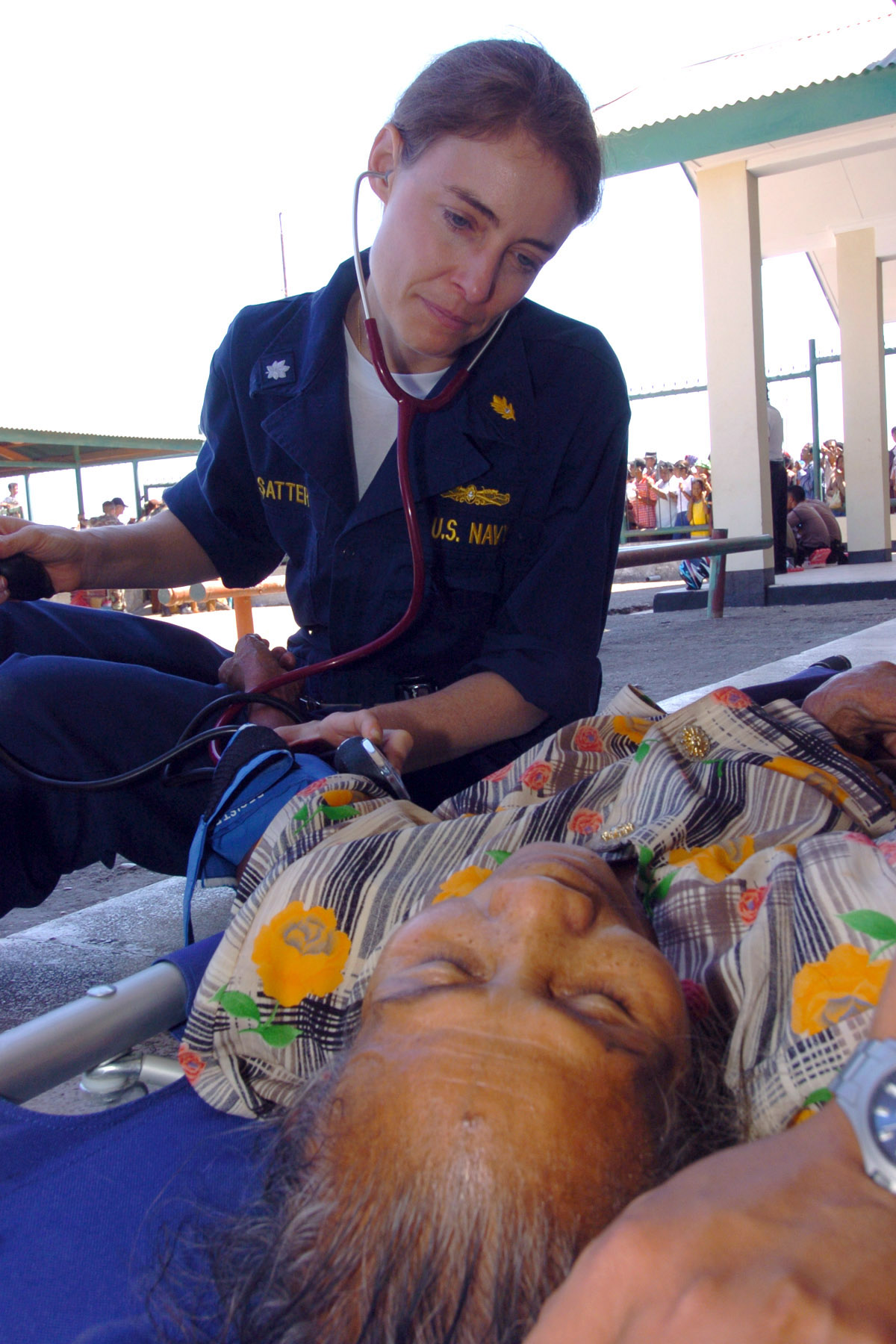
Syncope or fainting is the losing consciousness temporarily when the brain is deprived of adequate blood flow, oxygen, glucose. The brain needs the blood flow to function properly. Blood provides the brain with oxygen and glucose (sugar). The brain consists of two hemispheres, the cerebellum, and the brain stem which need to be supplied with blood. If blood does not reach any of these, fainting occurs.
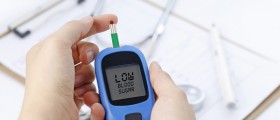
Fainting can be caused by a sudden drop in blood pressure, dehydration, insufficient blood, anemia, low blood sugar, and an inability of the heart to pump the blood into the brain. Before fainting, the person sweats, feels dizzy and weak, cannot hear and see properly, the muscles weaken and as a result a person falls to the ground. While unconscious, muscles may twitch which can be mistaken for seizures. After fainting, the person quickly recovers fully although slightly confused and weak. However, a person can also feel chest pains and nausea in the case of some more severe health conditions such as heart attacks. Head injuries are not the causes of syncope since fainting in this case is the result of a concussion.
Fainting is not a serious problem if it lasts for a short time and does not occur often. It is not a normal thing, though, so the person who faints should turn to a doctor so as to confirm the cause of the fainting. If the person quickly gains full consciousness and does not have any injuries, a doctor should be consulted for advice and further care. If the person who fainted injured their ahead or some other parts of the body, he or she should be taken to hospital immediately. When a person is not breathing and has no pulse, call 911 because the doctors must take care of them immediately with AED or CPR. The patient with fainting problems must be given oxygen and intravenous line placed to supply the blood with adequate agents. The patient must do heart examinations and blood tests to check the level of blood sugar. The underlying cause of fainting must be determined so as to proceed with adequate treatment.
After the fainting episode, the person can prevent fainting by sitting or lying down whenever he or she feels dizzy or weak. Older persons with low blood pressure should wait a second after changing position so as to avoid these problems. A regular intake of fluid reduces the risk of fainting. Certain medications can also cause fainting so the dosage has to be adjusted sometimes.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...