Hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia is the medical term for the disorder when the level of calcium in the blood is above normal. Calcium is necessary for the formatting of bones as well as for contracting muscles, discharging of hormones, and functioning of nerves and the brain. If the level of calcium is high above normal, that can have negative effects on these processes.
Overactivity of parathyroid glands, cancer, some medications such as lithium and thiazide diuretics, and taking calcium and vitamin D supplements in very high amounts are the most common causes of hypercalcemia. Dehydration is also one of the causes of hypercalcemia because calcium accumulates when there is no fluid.
Hypercalcemia can be mild or severe. It is often that mild hypercalcemia does not even have any symptoms. The most common symptoms of severe hypercalcemia are excessive thirst and loss of appetite, but nausea, vomiting, confusion, fatigue, and lethargy can also happen. Furthermore, constipation and frequent urination are also some of the symptoms of hypercalcemia. People who suffer from this disorder also may experience muscle weakness, abdominal pain, and pain in muscles and joints.
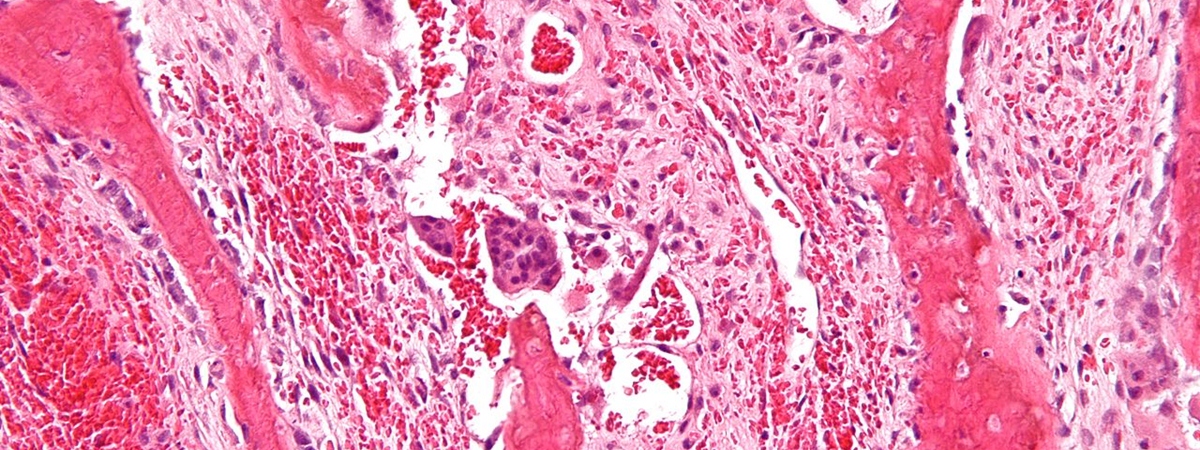
- Approximately 90% of people with hypercalcemia have primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT) or malignancy.
- Additional causes of hypercalcemia include granulomatous disease such as sarcoidosis, endocrinopathies such as thyroid disease, immobilization, genetic disorders, and medications such as thiazide diuretics and supplements such as calcium, vitamin D, or vitamin A.
- Hypercalcemia has been associated with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 protein inhibitors, immune checkpoint inhibitors, denosumab discontinuation, SARS-CoV-2, ketogenic diets, and extreme exercise, but these account for less than 1% of causes.
- Serum intact parathyroid hormone (PTH), the most important initial test to evaluate hypercalcemia, distinguishes PTH-dependent from PTH-independent causes.
- In a patient with hypercalcemia, an elevated or normal PTH concentration is consistent with PHPT, while a suppressed PTH level (
- Initial therapy of symptomatic or severe hypercalcemia consists of hydration and intravenous bisphosphonates, such as zoledronic acid or pamidronate. In patients with kidney failure, denosumab and dialysis may be indicated. Glucocorticoids may be used as primary treatment when hypercalcemia is due to excessive intestinal calcium absorption (vitamin D intoxication, granulomatous disorders, some lymphomas).
- Treatment reduces serum calcium and improves symptoms, at least transiently. The underlying cause of hypercalcemia should be identified and treated.
Complications of Hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia must be treated on time so it is important to consult the doctor if some of the symptoms appear untreated hypercalcemia can lead to very serious complications, such as osteoporosis, kidney stones, kidney failure, nervous system dysfunction, and arrhythmia.
Osteoporosis is the medical term for the thinning of the bones, which occurs when the bones release much calcium in blood. Osteoporosis, furthermore, can cause bone ruptures, spinal column curvature, and loss of height.
One of the complications that can occur if hypercalcemia is not treated is related to kidney stones. Renal lithiasis is the medical term for kidney stones, which are formed due to the accumulated calcium crystals in the kidneys. If these stones create a blockage, it can impair the kidney, and the passing of kidney stones is usually very aching.
In the case of severe hypercalcemia, kidney failure may also occur if the kidneys are seriously damaged. If kidney failure occurs, the last stage of renal disease is reached, and the person who suffers from this condition must take dialysis or transplant the kidney.
Hypercalcemia has negative effects on the nervous system because it can cause confusion, dementia, or coma, which can be mortal. Arrhythmia or abnormal heart rhythm is a condition that can be induced by hypercalcemia because it affects the electrical impulses that regulate the rhythm of the heart.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...