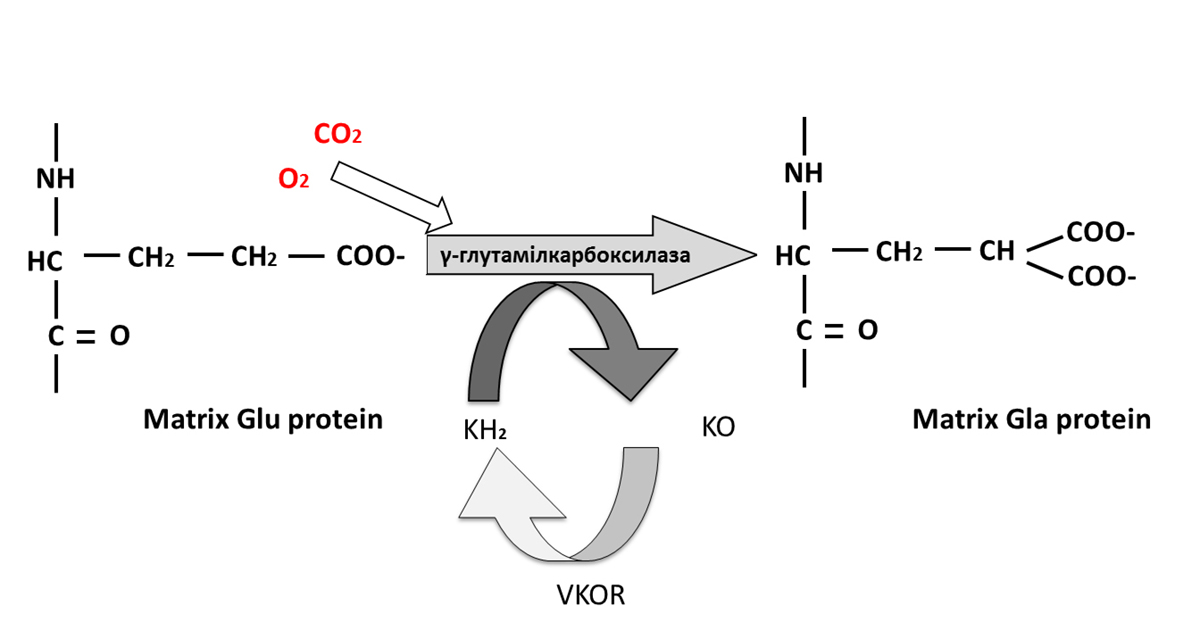
Vitamins K
Vitamin K is a fat soluble vitamin necessary for coagulation of the blood. Other fat soluble vitamins are vitamins D, E and A, while all other vitamins are water soluble (vitamins B, C). There are several types of vitamin K. K1 is phytomenadione and this is the vitamin K found in plants. K2, or flavinoquinone is produced in the large intestine by normal bacterial flora and K3 (menadione) is synthetic vitamin K.
Our body usually absorbs enough of vitamin K, but when antibiotics or some other therapy destroys intestinal bacteria, people are advised to increase the amount of food rich in vitamin K.
Food Rich in Vitamin K
There are many foods that are extremely rich of vitamin K. Some of these are: spinach (raw and cooked), Brussels sprouts iceberg, romaine or butterhead lettuce, spring onions, broccoli, cabbage, peas, cucumber, asparagus, parsley and celery.
Some foods also contain plenty of this vitamin and are highly appreciated as vitamin K sources. These include food such as: plums, prunes, rhubarb, soy beans and soy products. Bread and many salads are rich in vitamin K also, especially endive, beets, turnips, sauerkraut and coleslaw. If you need to enrich your diet with vitamin K some nutritionists advise using egg yolks, mayonnaise, butter, cheese and beef liver. However, if you don’t want to use these fatty products, you might switch to fresh fruits or vegetable salads.
When trying to increase the amount of vitamin K through your diet, remember that it is always better to eat raw or slightly fried food, than cooked. Just a little bit of cold pressed oil added to your vegetables will ensure the nutritive value of your food. Once you blanched your vegetables, don’t throw the cooking water, because it might be valuable stock for a soup or any other dish.
Vitamin K Toxicity
The recommended daily dose of vitamin K is around 65mg for adult women and bit higher, around 80mg for adult men.
Allergic reactions were reported by some people to vitamin K supplements, but there were not a single report of toxicity to vitamins K1 or K2. The synthetic form of vitamin K3 in large doses is known to cause allergies, liver toxicity and hemolytic anemia. Because of that, vitamin K3 is not on the FDA list of vitamins allowed in OTC (over the counter) preparations.
Vitamin K Deficiency
Lack of vitamin K in the body may cause nose and other bleeding, arterial problems, malnutrition, osteoporosis and inflammatory bowel disease. Some medical conditions and drugs are known to cause vitamin K deficiency. Antibiotic medications, antiepileptics, anti-cholesterol medications, liver and gallbladder problems may all cause lack of vitamin K in the body.
Newborn babies might suffer from vitamin K deficiency also, which is why many doctors recommend injections of vitamin K1 at birth and during the first month of a baby’s life.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...