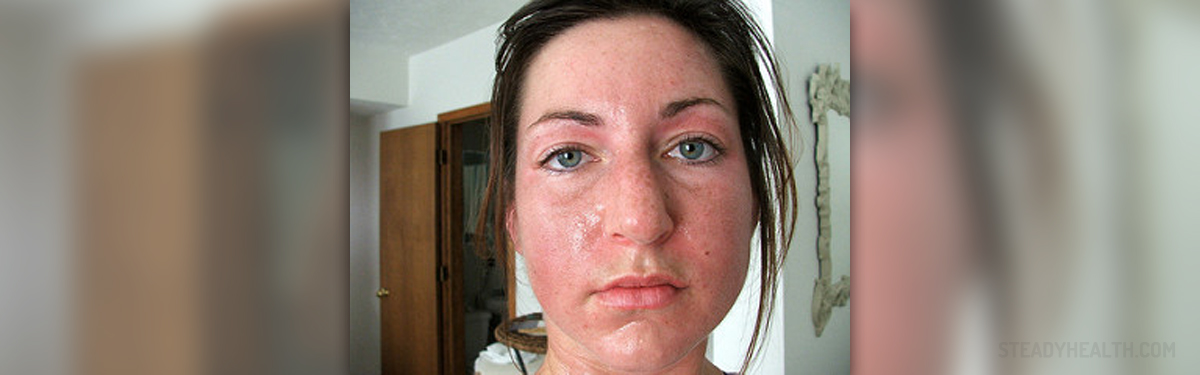
The average, and normal, human body temperature hovers at around 36 degrees Celsius, which would be 98.2 degrees Fahrenheit, with some individual differences being expected.
The body does regulate its own temperature to accommodate differing circumstances, and small fluctuations are absolutely typical and expected.
Your body functions quite effectively to release heat if there is a high body temperature. and in case of a low temperature, the body is able to generate heat to a certain extent. A person's body temperature can fluctuate due to environmental conditions and this is considered normal — however, an abnormal and more extreme fluctuation of your body temperature may point to the presence of an underlying medical condition which needs to be diagnosed and treated as soon as possible.
Body temperature fluctuations: What is normal?
In hot conditions, our body controls its temperature by inducing increased sweating. Excess sweat evaporates, a process that facilitates the cooling of the surface of the skin.
On the other hand, in cold weather, a body tries to maintain an adequate body temperature by preserving heat. The blood is transferred from the small capillaries within the periphery of the body to the inner warm parts in this case, and the brain sends massages to muscles to start shivering. Shivering may generate heat and maintain a higher body temperature for a certain period of time.
The normal fluctuation of the body temperature is between 97.0oF to 100.00F. If the fluctuation you are seeing exceeds these limits, there is a reason for concern.
Causes of a fluctuating body temperature
Fluctuation of body temperature is associated with certain physiological processes, and it may also be a symptom of certain illnesses.
For example, fluctuation of body temperature is typical during periods of rapid body growth. It increases within the first or second day after a person's birth and then it decreases slightly to the middle age. In elderly people, body temperature again slightly increases.
Circadian rhythms — representing your "internal body clock" — are related to a change in body temperature, in accordance with periods of physical activity and rest or sleeping. The drop in body temperature in this case occurs between the hours of 3 and 5 AM and 1 and 4 PM.
Temperature fluctuation is also connected to hormonal changes. This particularly occurs in women, during menstruation and ovulation. Fluctuations in body temperature caused by hormonal changes may also affect pregnant women.
Abnormal fluctuation of body temperature is a typical feature of many infections and other diseases. These would include injury, trauma, arthritis, and brain tumors, but also conditions like diabetes and hypothyroidism. Even the use of certain medications may cause body temperature fluctuations. And finally, a fluctuation of body temperature quite normally occurs after you consume meals (after which the body kicks into a digestive process) and is always associated with consumption of alcohol and physical exercises.
Consequences of a fluctuating body temperature
If the body temperature becomes excessively high, a situation more commonly referred to as a high fever, the person may suffer from intensive headache, dizziness, confusion, cardio-respiratory collapse, seizures, shock and in some cases there is a change of severe damage to the brain.
On the other hand, an excessive reduction in body temperature leads to reduced reflexes or complete loss of reflexes, shallow breathing, serious arrhythmias and respiratory arrest.
- medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001202.htm
- medlineplus.gov/ency/article/004019.htm
- Photo courtesy of Sarah (Rosenau) Korf by Flickr: www.flickr.com/photos/sarahrosenau/137089824/













Your thoughts on this
Loading...