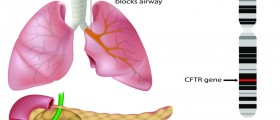
Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disorder characterized by the body’s production of abnormally thick and sticky mucus. This chronic inherited disease affects the epithelial cells that line the passages in the organs of the body. Cystic fibrosis mainly affects the lungs and the digestive system.
Cystic Fibrosis Overview
Normally, cells in the epithelium secrete thin and watery mucus that serves as a lubricant and aids in protection of the body organs. However, in people with cystic fibrosis mucus is thicker and accumulates in the channels of different body’s organs leading to infections and other complications.
The lungs and the pancreas are particularly affected by this disease. Therefore, primary symptoms of cystic fibrosis are breathing and digestive problems. Breathing problems occur as mucus builds up in the lungs, keeping trapped germs in the organ and resulting in an infection.
Digestive problems are caused by clogged passage between the pancreas and the intestines. Because of this, an individual with cystic fibrosis has difficulty digesting food and absorbing vitamins and nutrients. The liver, sweat glands and reproductive organs can also be affected by cystic fibrosis.
Causes of Cystic Fibrosis
Men and women are equally affected by cystic fibrosis. The disease is diagnosed in approximately 30,000 people in the United States. Cystic fibrosis occurs due to mutations in a gene on chromosome 7, which produces a protein known as cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (CFTR). In people with cystic fibrosis, this gene makes a defective form of the CFTR protein leading to a production of thick and sticky mucus.
Two copies of the CFTR gene are required for development of cystic fibrosis. This means that both parents of the affected person must be carriers of the disease. However, when two carriers of cystic fibrosis have a child, the child has a 1 in 4 chance of inheriting the disorder. Cystic fibrosis is the most common in Caucasians of northern European descent. On the other hand, Asian Americans have the lowest risk of cystic fibrosis. Symptoms of Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is usually diagnosed by the age of 2 but in some people it may not be identified until adolescence when cystic fibrosis is of milder form. Cystic fibrosis in infants causes intestinal blockage, poor growth, failure to gain weight, persistent cough with mucus, wheezing, foul smelling stool, diarrhea, salty sweat, nasal polyps, fatigue and frequent sinus infections. Individuals with cystic fibrosis frequently have lung infections and are susceptible to other illnesses such as diabetes and osteoporosis.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...