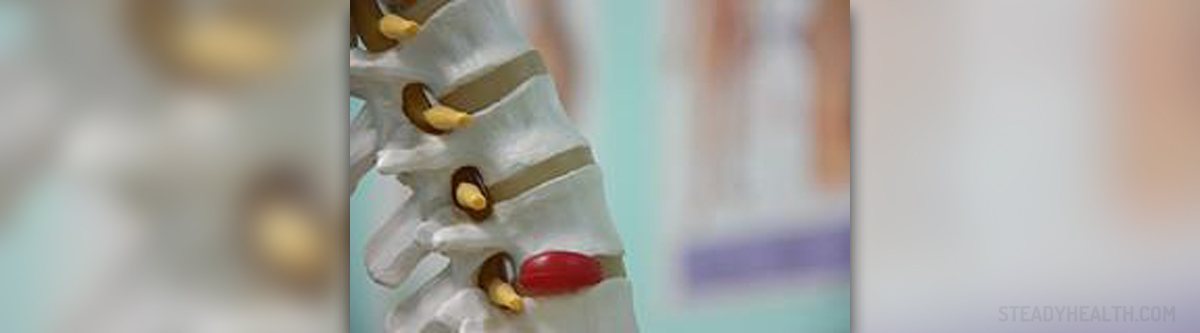
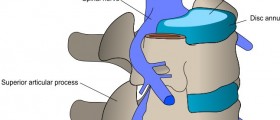
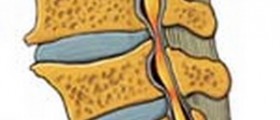
The spinal column is a body part that comprises a series of individual bones known as vertebrae. These bones are classified into several groups depending on the level so there are seven cervical vertebrae, twelve thoracic vertebrae, five lumbar vertebrae and finally five sacral and 4 coccygeal vertebrae. Sacral and coccygeal vertebrae are fused while the rest of these bones are separated by a disc. Spinal disc is of major importance and plays a significant role in cushioning movement of the spine, preventing damage to the nearby vertebrae and structures that pass through the space between the adjacent vertebrae (e.g. spinal nerves, blood vessels etc.). Each and every disc has a nucleous pulposus (a gel-like center) and an annulus fibrosus, a firm ring-like structure that surrounds the soft middle part of the disc. Disc herniation is a serious condition in which the soft center of the disc protrudes through a weakened or torn annulus fibrosus. As a result, a person develops certain symptoms and signs all of which are connected with direct irritation or compression of the nearby structures, predominantly spinal nerves. Disc herniation may occur at all levels of the spine but it is mostly reported in the lumbar and cervical area.
Problem with Herniated Disc
It is estimated that arm pain associated with cervical disc herniation actually is the most common medical issue treated by spine specialists. Cervical disc herniation is a condition that generally affects people between 30 and 50 years of age. It is either triggered by some sort of trauma or injury to the cervical portion of the spinal column or it develops spontaneously due to underlying degenerative changes of the spine and its components.
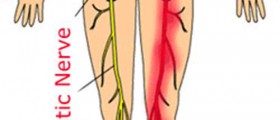
The protruded disc is blamed for irritation and compression of the cervical spinal roots. All the mentioned precipitates pain that typically radiates along the nerve pathway down the arm. Numbness ad tingling sensation occur as well. The most severe cases of cervical disc herniation are characterized by muscle weakness. In the majority of cases herniation takes place at the C5-C6 level and then at the C6-C7 level. Also it may occur at the C4-C5 level and finally, in rare instances at the C7-Th1 level.
When it comes to symptoms and signs patients typically experience, these may vary according to the level of herniation as well as severity of the spinal nerve irritation/compression. In case C5 is affected, patients experience pain in the shoulder, weakness in the deltoid muscle and generally have difficulty moving the upper arm. There is no tingling or numbness. Irritation/compression of the C6 root is characterized by weakness in the biceps and wrist extensor muscles. There is tingling and numbness both of which affect the thumb side of the hand and are accompanied by pain. Weakness of the triceps and finger extensor muscles are typical for irritation or compression of the C7 root. Numbness and tingling spread down the triceps muscle and reach the middle finger. And finally, if the C8 root is affected, patients have problems with hand grip while tingling and numbness radiate towards the little finger and the side of the hand.
Surgical Procedure to Help Herniated Disc
Even though initially all patients undergo conservative treatment, those who simply fail to respond to non-invasive treatments require surgery. Surgery is also the first treatment option for patients in whom symptoms get progressively worse within short period of time as well as individuals with progressive neurological decline. Depending on different factors surgeons may opt for microdiscectomy, laminectomy or foraminotomy. Cervical spinal fusion is also an option.
In case of microdiscectomy surgeons remove fragments of the herniated disc and this is achieved only with the assistance of an operating microscope. Furthermore, laminectomy is a procedure during which the part of the bone or the tissue (the disc and its components) responsible for the pressure on the nerve or the very spinal cord is removed. Laminectomy requires hospitalization of at least two days and is always performed under general anesthesia. Foraminotomy relieves pressure on spinal nerves due to compression caused by nearby bones, disc protrusion or the presence of scar tissue. The very decompression takes place at the intervertebral foramina, hence the name of the surgery.
Cervical spine fusion is a rather complex surgical procedure. It requires bone which can be taken from other parts of the body or the surgeon uses a bone graft obtained from a bone bank, metal implants which hold the vertebrae together and metal plates that are screwed into the bone and hold the adjacent joints together. The degenerative disc is easily removed and the adjacent vertebrae fused. The surgeon reaches the disc and performes fusion through an incision at the front or the back of the neck. Patients are released after several days and they should wear a brace/cervical collar throughout the recovery. Cervical fusion is associated with several risks some of which are pain in a bone graft site, failure of the fusion, breakage of metal implants, deep vein thrombosis, spinal cord/nerve injury, graft rejection, infections, excessive bleeding and risks of general anesthesia.



-Causes,-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)



-Test-And-What-Do-The-Results-Mean_f_280x120.jpg)
Your thoughts on this
Loading...