
Epidermolysis bullosa is a group of disorders that occur mainly in response to mechanical trauma. Epidermolysis bullosa can lead to the formation of blisters, and in the past, Epidermolysis bullosa has been categorized according to skin morphology.The wound healing process is often impaired by foreign bodies, nutritional deficiencies, bacteria, aging, and tissue anoxia.
In order to control the healing of wounds during the onset of Epidermolysis bullosa, it is necessary to control all of the above factors. Those with this condition tend to heal slowly, perhaps because of defect in laminin five.
Infection
Patients with Epidermolysis bullosa might suffer from immunologic abnormalities. This can lead to a lowering of lymphocyte production, or poor nutritional status. As a consequence of this, there might be a lowered resistance to infection. The normal causative organisms in this regard are staphylococcus aureus and streptococcus pyogenes. There is the also the possibility of the occurrence of infections like pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Epidermolysis bullosa patients might also have a vulnerability towards the development of sepsis.
With regard to infection, prevention is the preferred approach. With regard to areas of crusting and denudation, it is necessary to undergo a strict regime of wound care. This might require the employment of whirlpool therapy and the administration of topical antibiotics.
Tumors
In those who do not suffer from Epidermolysis bullosa, cutaneous SCC generally arise mainly in areas that are regularly exposed to the sun. SCC primarily affects those with skin types I and II. However, those with Epidermolysis bullosa will have a different distribution of their cutaneous SCC. With regard to Epidermolysis bullosa, SCC can occur in people of all skin types. The peak incidence of SCC will tend to increase greatly in those who are in the second and third decades of life. Cutaneous SCC is thought to arise as a result of the retaining of type VII collagen.
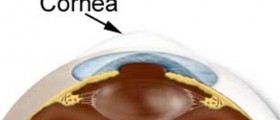
Eye lesions might be experienced by those with Epidermolysis bullosa. Recurrent blepharitis in one or both eyes, as well as bullous conjunctivae lesions, might occur. Those suffering from Epidermolysis bullosa are likely to experience problems such as corneal ulcerations, corneal scarring, eyelid lesions, and the obliteration of the tear ducts. In those who have the recessively inherited Epidermolysis bullosa Hallopeau-Siemens subtype, cicatricial conjunctivitis might also occur. Corneal problems are treatment with the use of antibiotic ointment and cycloplegic agents. This approach aims to reduce ciliary spasm, and to provide comfort for the patient.











-What-Are-Your-Options_f_280x120.jpg)
Your thoughts on this
Loading...