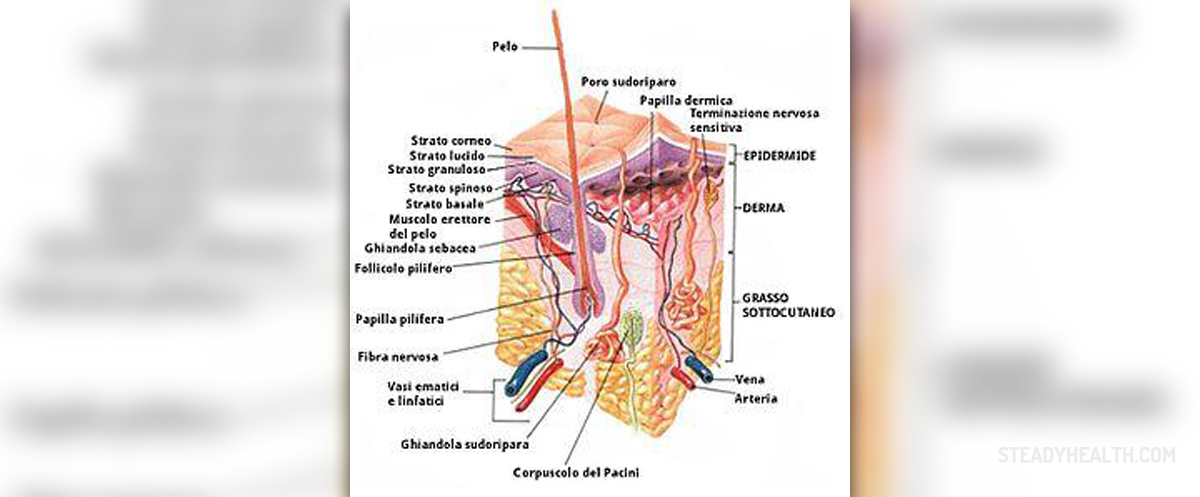
Out of many different skin disorder humans may be suffering from, epidermolysis bullosa is definitely one of the most severe ones. This skin condition is associated with uncontrollable blistering of predominantly skin even though other internal organs such as the esophagus may be affected. Skin blistering, scarring and all the associated complications occur due to increased sensitivity of an individual towards minor skin trauma, skin irritation and friction.
Epidermolysis Bullosa Types
Experts have managed to determine four main types of the disease, dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, epidermolysis bullosa simplex, hemidesmosomal epidermolysis bullosa and junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Apart from these a person may also develop epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, which is actually an autoimmune disorder and a bit different form from the previous four.
It may be quite challenging to identify the actual type of the disorder because each of the mentioned 4 types has many subtypes. For instance, Weber-Cockayne is a common subtype of epidermolysis bullosa simplex. Patients with this disease experience only blistering of their palms and soles and may additionally suffer from excessive perspiration.
Different types of the disorder are characterized by different pattern as well as the severity of blistering. Also, the onset of disease may vary so some people are born with skin lesions while others may develop blisters once they enter adolescence or even adulthood.
Most types of epidermolysis bullosa develop in a form of either autosomal dominant or recessive pattern of inheritance.Diagnosing Epidermolysis Bullosa
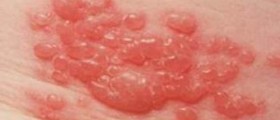
The hallmark of epidermolysis bullosa is the formation of large skin blisters. These are distributed on different parts of the skin and may also affect certain internal organs. The very presence of skin blisters may be a reason why the doctor assumes the person is suffering from epidermolysis bullosa. However, clinical findings may not be sufficient enough to confirm the disease.
This is why doctors opt for additional tests and exams. Firstly, they take samples of the affected skin (perform biopsy) and send samples for pathohistological examination. This examination may reveal detachment of the epidermis from the dermis, which is actually a characteristic of the disease.
Also, genetic testing is of major importance and may be quite a sufficient test for confirmation of epidermolysis bullosa.
In order to differentiate standard types of epidermolysis bullosa from epidermolysis bullosa acquisita doctors opt for special skin tests.
Once the disorder is confirmed, additional tests and exams are performed to evaluate damage to the body and confirm and assess the extent of complications. After that patients may start with the most convenient treatment.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...