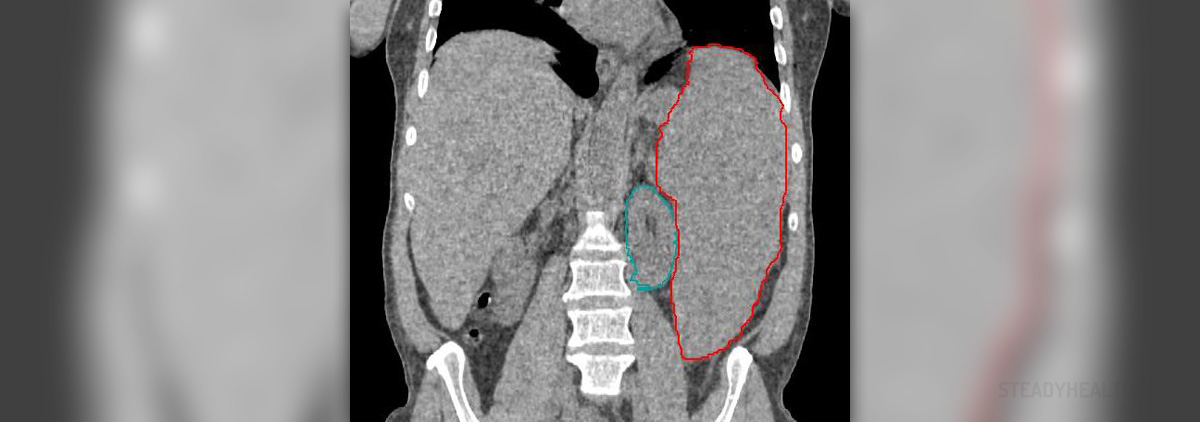
Splenic Enlargement
The spleen is an abdominal organ localized in the upper part of the left abdomen right below the rib cage. It is normally the size of a fist and can get enlarged in a variety of medical conditions. Many people are not even aware of the enlarged spleen and this condition can be found accidentally during physical examination of a patient. The goal of the treatment in case of enlarged spleen is to bring the underlying condition under control. This way the spleen will reduce in size.
The most susceptible group for spleen enlargement includes children suffering from mononucleosis. Still, the spleen can get enlarged in all people. The spleen is regularly enlarged in people of African descent who suffer from sickle cell anemia. Even people of Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry who are more prone to Gauchers diseases and Niemann-Pick disease suffer more from enlarged spleen. And finally, people who are traveling to countries in which malaria is endemic carry higher risk of splenic enlargement.
Diagnosing Splenic Enlargement
Enlarged spleen can be easily found by simple palpation of the abdomen. Gentle physical examination of the left upper abdomen is required because enlarged spleen is highly susceptible to rupture.
Additional investigation includes blood test and ultrasonography or CT scan of the abdomen. In some cases even MRI is indicated. Doctors will perform additional test to establish the underlying cause of the splenic enlargement. They include liver function tests and pathohystological examination of the bone marrow. The material from the bone marrow is obtained either by a bone marrow aspiration or a bone marrow biopsy.
Treatment for Splenic Enlargement
The doctor basically treats the underlying cause of splenic enlargement. In infections the patients are given antibiotics and the spleen eventually regains its normal size. In case of splenic enlargement cause by Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's disease the therapy includes chemotherapeutics and radiation therapy.
If doctors cannot identify the underlying cause or if the enlargement can lead to serious complications such as rupture of the spleen, this organ is surgically removed. The removal of the spleen is sometimes excellent treatment and may lead to alleviation of the symptoms and signs of the primary disease.
The infection after the surgical removal of the spleen can be successfully prevented by a serious of vaccinations prior and after splenectomy. These vaccines prevent diseases such as pneumonia, meningitis and infection of other organs including bones, joints and the blood. The infection is additionally prevented by antibiotics.
People whose spleen is enlarged need to avoid sports of any kind especially contact sports and to keep away from strenuous activities since all of these may cause the spleen to rupture.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...