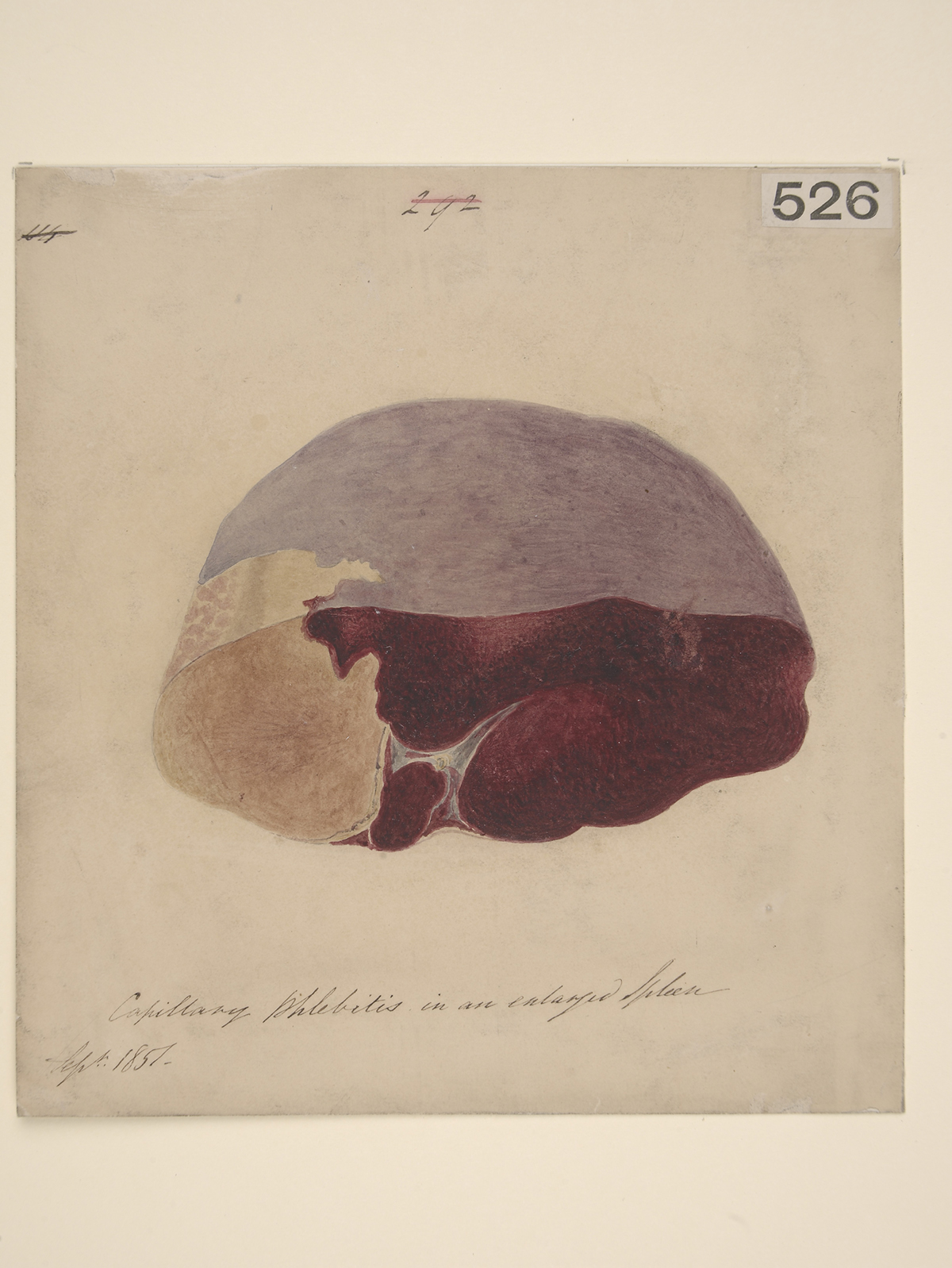

The spleen is a small abdominal organ, normally the size of a fist. However, in many medical conditions the organ can enlarge and such change is medically known as splenomegaly. Even though the spleen can significantly enlarge the condition may remain asymptomatic. It is essential to identify the enlarged spleen as well as the underlying cause and treat the patients accordingly. This way the primary illness is brought under control and all potential complications of spleen enlargement can be prevented.
The spleen filters and destroys old and damaged blood cells, prevents infections from occurring and stores red blood cells and platelets. In case of its enlargement these functions can be damaged and the consequences can be disastrous.
Clinical Characteristics of Enlarged Spleen
As it has already been said some people have no symptoms at all. On the other hand, if there are symptoms they usually include pain or fullness in the left upper abdomen that may spread to the left shoulder. Some patients fell full after eating small portions of food. Enlarged spleen also leads to anemia (low number of red blood cells), fatigue, increased susceptibility to infections and easy bleeding.
What Are Causes of Enlarged Spleen?
There is a whole variety of infections as well as other illnesses associated with enlarged spleen. For example, enlarged spleen is a characteristic of several viral infections and infective mononucleosis is only one of them. Even some bacterial infections may cause spleen enlargement. Syphilis and endocarditis are two bacterial infections that may be responsible for enlarged spleen. Furthermore, enlarged spleen occurs in patients suffering from malaria, one of many parasitic infections.
Apart from infections enlarged spleen also affects people suffering from many other illnesses such as cirrhosis, various types of hemolytic anemia, blood cancers (leukemia and lymphomas) and metabolic disorders (Gaucher's disease, Niemann-Pick disease etc.). And finally, the spleen may enlarge in case there is pressure on the veins of the spleen or liver or there are clots inside these veins.
Treatments for Enlarged Spleen
In case there is a risk of serious complications or some of them have already developed the organ is surgically removed (splenectomy). Surgery is also performed in case of chronic spleen enlargement. It is essential to mention that elective splenectomy carries several risks such as a risk of life-threatening infections including post-splenectomy infection. Patients are postoperatively administered with antibiotics. In case a person has undergone splenectomy the risk of infections can be reduced with a series of vaccinations. Vaccines are administered prior to and after the surgical removal. Some of the vaccines administered to such patients are the pneumococcal vaccine, meningococcal vaccine and haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine. Enlarged spleen can also reduce thanks to radiation therapy.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...