About coeliac disease
Coeliac disease, also called gluten enteropathy or coeliac sprue, is a life-long condition affecting the small intestine, and it is related to gluten.
Gluten is a mixture of proteins called gliadin and glutenin. It is found in wheat, oats, barley and rye. In people who have coeliac disease, the body cannot tolerate gluten, or more precisely, it releases antibodies that react to its presence in an adverse way. These antibodies attack the lining of the intestine, affecting the way in which food and nutrients are absorbed.
This disease can be diagnosed at any age but it is generally first noticed in babies, when cereals are first introduced in their diet.
The symptoms of coelic disease can be quite subtle and a person can only feel slightly unwell, which is why it may take some time to diagnose it.
The surface of the intestine lining contains small, finger-like structures called villi. They play a very important role in the absorption of nutrients from the food. When gluten comes in contact with the lining of the small intestine, the antibodies produce a reaction which gradually leads to destruction of the villi. This results in malapsorption, meaning that the food is passed without being properly absorbed, which, in turn, leads to malnutrition, anemia, diarrhea, osteoporosis, nutritional deficiencies and other problems.
Coeliac disease can only be managed by completely excluding all foods containing gluten from the diet. Gluten-free diet leads to significant improvement and even reverses the damage to the lining of the intestine. However, if gluten is re-introduced in the diet at any point in life, the symptoms and malapsorption problems will start again.
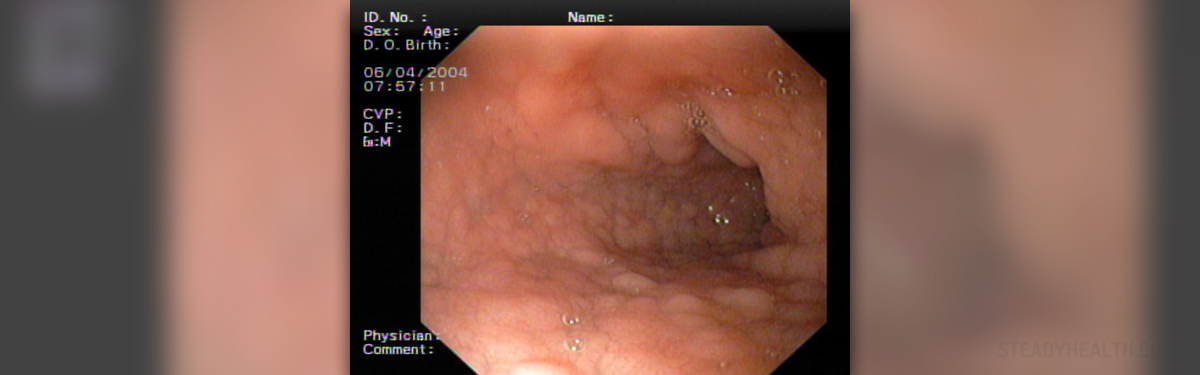
Endoscopy for coeliac disease
The diagnosis for coeliac disease is based on several tests. Physical exam is the first step towards the diagnosis, followed by some questions about eating habits and bowel movement. During the physical exam, doctors usually examine the abdomen through palpitation and check the mouth for ulcers. Blood tests are done in order to check the levels of certain nutrients, such as iron, calcium and folic acid and also to determine the presence of antibodies.
However, in order to confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to perform endoscopy test. Endoscopy is a diagnostic procedure that can be done under total anesthesia or with the use of an anesthetic spray that numbs the throat. A thin, flexible tube, with a small camera attached to one end, is introduced through the mouth. The camera is guided through esophagus and stomach towards the small intestine, where it takes images of the lining. The tube also contains a clipper which can be used to collect a small biopsy sample of the lining, which is then send for analysis.
The entire procedure does not last longer than 10 or 15 minutes and it is generally painless, especially because anesthetic is used. Some discomfort, however, is to be expected.

















Your thoughts on this
Loading...