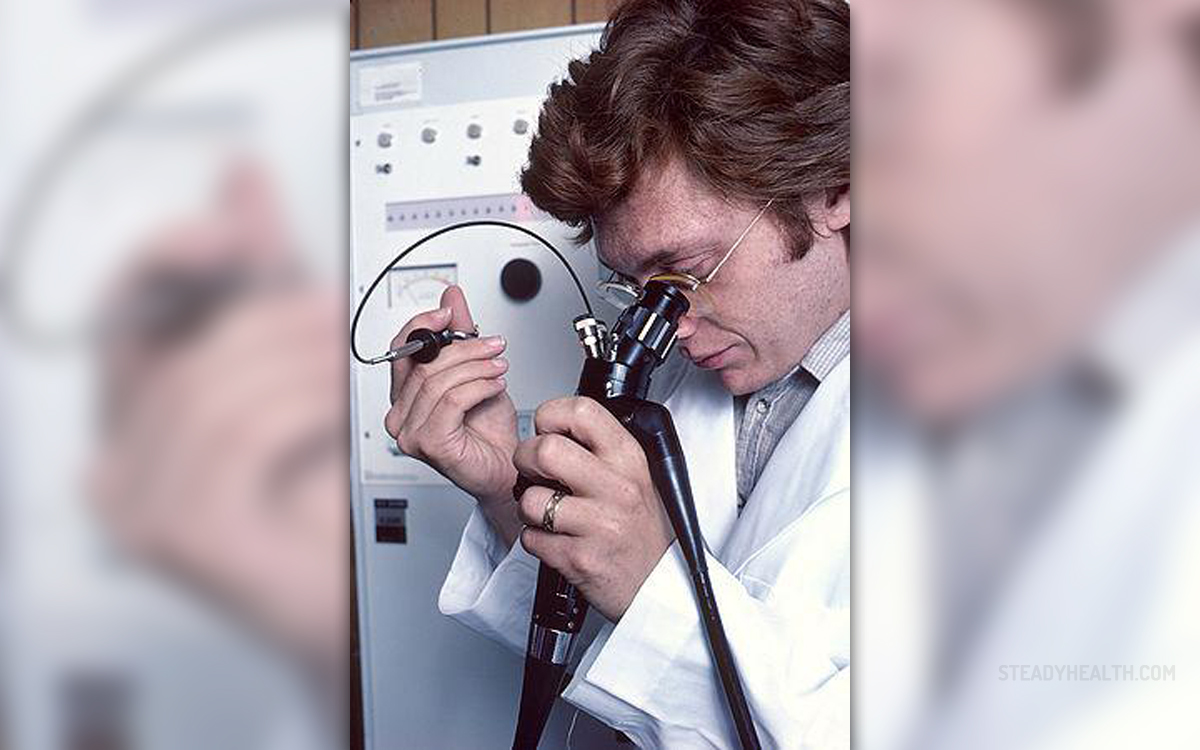

Endoscopy is a powerful tool when it comes to diagnosing a variety of gastrointestinal disease, gastrointestinal bleeding and even treatment of certain conditions. Safety and clinical efficacy of the procedure have been established. However, safety of the procedure performed in pregnant women is still disputable. For instance, gastrointestinal bleeding and cholelithiasis are indications for endoscopy in non-pregnant women. What complications are associated with diagnosing these condition during pregnancy with endoscopy have not been completely identified.
It is estimated that approximately one pregnant women per year has strong indications for undergoing endoscopy. However, the procedure is performed in more than just one pregnant women. This approach is more appropriate comparing to barium radiography because radiography is teratogenic i.e. may cause severe damage to the unborn baby.
Endoscopy during Pregnancy
Premature labor and teratogenesis are two major problems doctor have to face with when determining whether a pregnant woman should or should not undergo endoscopy. The very procedure may cause fetal complications since it is associated with medical teratogenicity, placental abruption and transient hypoxia. Hypoxia is the major cause of damage to the fetus. Also hypotension may cause inadequate blood supply to the placenta and also induce fetal hypoxia.
Hypoxia during endoscopy is possible due to administered medications, vagally mediate bronchospasm and problems with the larynx induced by intubation. Pulmonary aspiration is also a problem that leads to hypoxia. In case of sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy intravenous sedation and neurohumoral responses may initiate lack of supply of oxygen to the baby.Estimating the Safety
By taking into consideration safety while performing endoscopy the doctor may eventually opt for the procedure. It is sometimes hard to make correct decision. Some fetal risks are minimized by reducing, substituting or even avoiding medications that have teratogenic potential while performing endoscopy. Furthermore, it is essential to perform complete fetal and maternal assessment prior to the procedure.
All limitations of endoscopy during pregnancy must be fully understood and recognized.
To sum up, endoscopy during pregnancy carries certain risks which simple cannot be neglected. The risks are especially important to be taken into consideration during organogenesis in the first trimester. In that period the fetus is most susceptible to teratogenic medications. Also, there is a risk of placental abruption from endoscopic intubation. Finally, there is a risk associated with transient intraprocedural maternal hypotension, hypoxia and cardiac arrhythmias. Some of potential complications that develop due to the procedure are premature delivery, stillbirth, low birth weight, neonatal illness, congenital malformations and neurodevelopmental deficits. All the mentioned influence the final decision doctor makes regarding the procedure.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...