Endometriosis - Overview
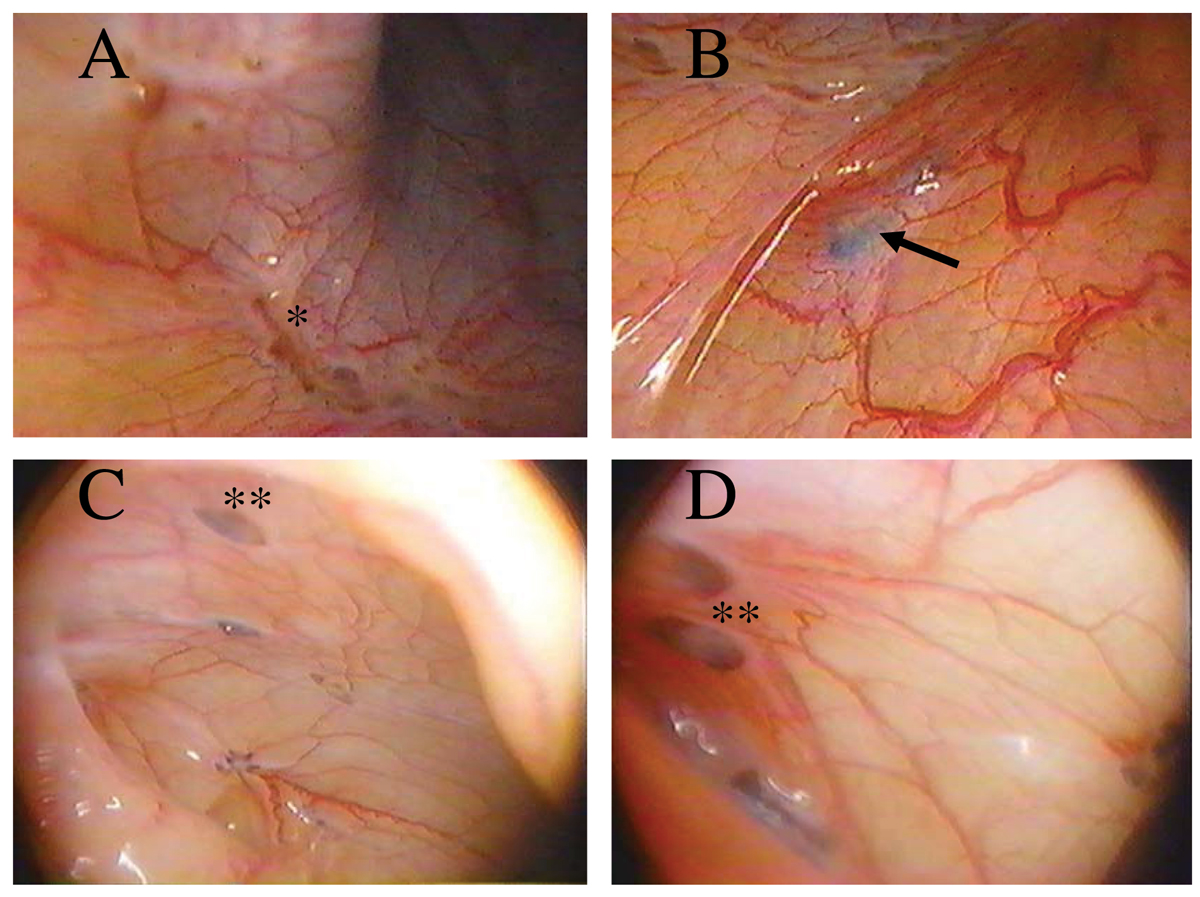
Endometriosis is a serious medical condition associated with the abnormal growth of the cells that normally line the inner surface of the uterus. This abnormal growth occurs in different locations outside the uterus. Some organs that may be affected with the excessive growth of endometrial cells include, the ovaries, the fallopian tubes, the outer surface of the uterus, intestines etc. Apart from these sites, a clusters of these cells can be also found on the surface lining of the pelvic cavity, the vagina, cervix and bladder. Even though endometrial implants are not considered malign they may cause excruciating pain. Furthermore, the condition is associated with infertility and requires a medical diagnosis and appropriate treatment. The pain due to endometriosis can be very intensive causing many women to search for appropriate pain relieving alternative.
Endometriosis Pain Relief
There are several medications which may effectively reduce, if not eliminate, pain in women suffering from endometriosis.
The first line of medications includes non steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs). Apart from being highly effective in pain management NSAIDs are also very efficient in alleviation of inflammation. Among these medications are drugs which are more potent in reduction of pain and others which predominantly reduce inflammation. NSAIDs can be prescribed and are also available over-the-counter. Some of NSAIDs used in endometriosis are Aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, ketoprofen etc. It is essential not to take any of the medications which contain codeine since this substance may lead to pelvis congestion and constipation which may only aggravate already unbearable symptoms.
GnRh (gonadotropin releasing hormone) agonists are also a group of medications which have become widely used for pain management for women suffering from endometriosis. These medications are able to change the natural hormone levels in the body and are chemical inductors of menopause. The effects include shrinking of the endometriosis implants and subsequent reduction in pain. Eve though GnRh agonists are very effective in pain management they also carry a significant number of side effects. This is why the treatment with GnRh should not last longer than 6 months.
The pain can be also controlled with any medication or a hormone (such as progestin) which is able to stop menstrual periods. Unfortunately, this is not a long- term solution and can only temporary manage pain caused by endometriosis implants. Progestin, for example, is not a good solution since it has several side effects such as bloating, weight gain, depression and irregular vaginal bleeding. Furthermore, it may lead to problems with ovarian function long after it is discontinued.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...