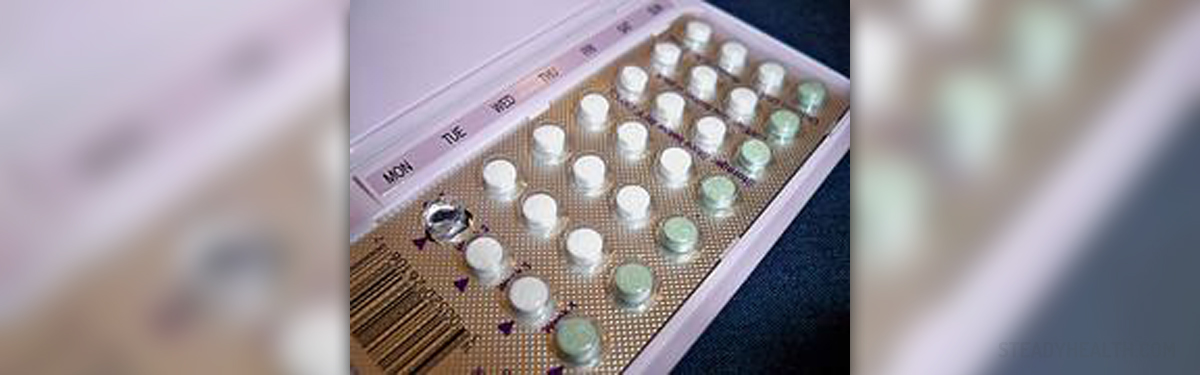
Birth control pills are also known as oral contraceptives and they commonly contain progestin and estrogen. Their main function is to prevent unwanted pregnancy, because they affect endometrium’s monthly cycle and its growth, bleeding and shedding. Besides affecting normal endometrial tissue, contraceptive pills also affect misplaced endometrium, found in different parts of the body in patients suffering from endometriosis.
How Contraceptives Help with Endometriosis?
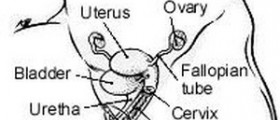
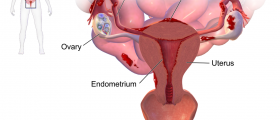
As mentioned, oral contraceptives affect all endometrial tissue. In case of abnormal endometrium, found in the ovaries, fallopian tubes of other places in the abdominal cavity or body, birth control pills can shrink these endometrial implants and make them bleed less. This treatment can also be used after endometriosis surgery, to slow down or completely stop the growth of residual abnormal endometrial tissue.
In many cases, the contraceptive pill is the first choice of treatment for pain caused by endometrial growth. Although the pill represents hormone therapy, this is the least likely to cause any problems and can be used for several years. Other hormone treatments are prescribed for several months up to 3 years only, because of adverse effects they cause.
Sometimes, birth control pill can be combined with NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), to be more effective. These pills are found to significantly improve endometriosis symptoms in mild cases, but they cannot cure this problem. Seasonale contraceptive pills (used for 84 days) are those used for the treatment of endometriosis.
However, you should know that contraceptive pills will not treat infertility if you happen to suffer from this problem due to endometriosis. For that reason, you need to use different medications, so consult your doctor about this issue.Possible Health Problems
The most common problem in women treated for endometriosis is recurrent pain after discontinuation of hormone treatment (birth control pills). One year after the treatment pain returns in some 20% of treated women, while 37% of them treated for mild endometriosis experience pain 5 years after the treatment. In women treated for severe symptoms of endometriosis, 5 years after the therapy pain returns in 74% of cases.
Besides recurrent pain, these patients may also experience different adverse effects of the pill, such as menstrual changes, headaches, weight gain, tenderness of the breasts, nausea and vomiting. Some of these problems are found in the first months of treatment, but they can persevere throughout the therapy. Women can also notice darkening of the skin in certain areas of the face, especially after exposure to the sun and also some sexual problems such as decreased interest in sex.
ACHES symptoms represent rare and serious complications, which should be immediately reported to the doctor. They include A – severe abdominal pain, C – chest pain, H – headaches or migraines, E – eye problems.
Contraceptive pills are not recommended to women older than 35 years of age, those with uncontrolled diabetes or hypertension, women suffering from liver disease or have a history of conditions like migraine headaches, breast cancer, stroke or venal blood clots.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...