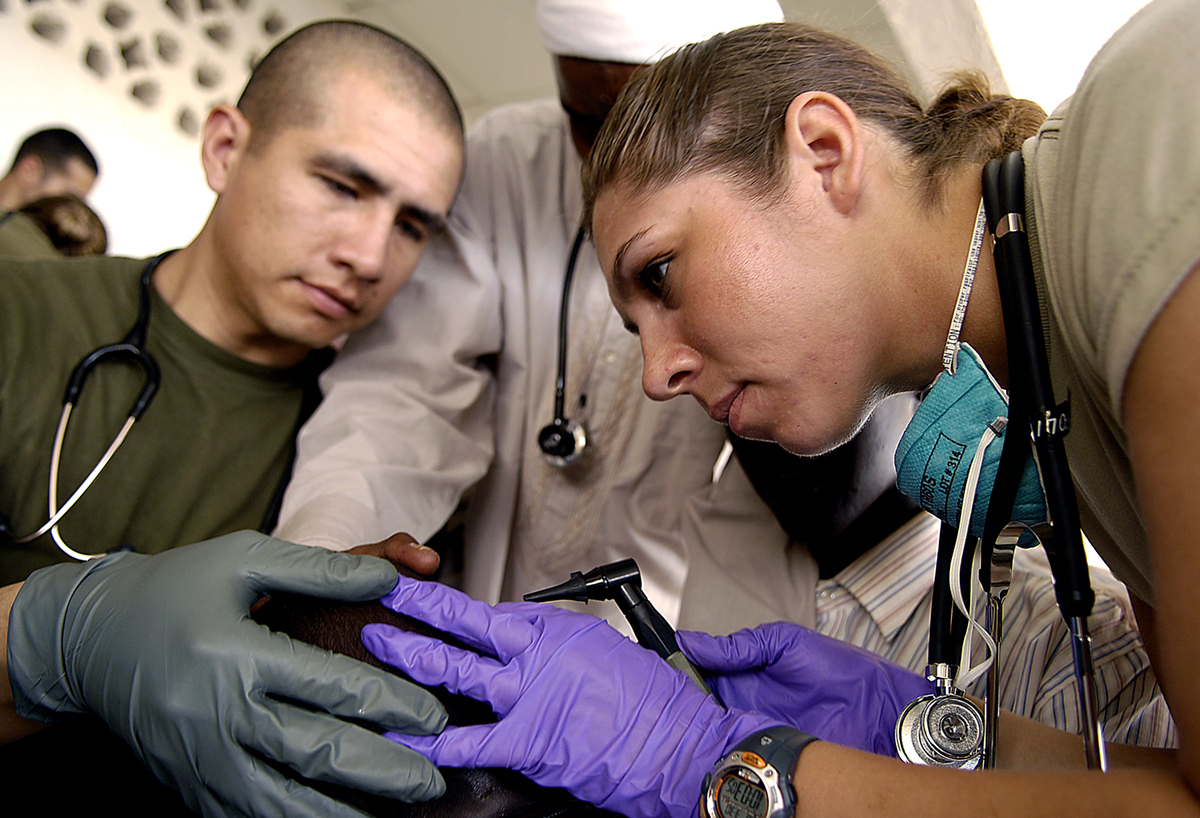

Ear Infection in Toddlers - Overview Ear infection in toddlers is very common and is actually the second most common infection in children after common cold. It is medically known as otitis media. Approximately 30-50% of all toddlers have experienced at least once ear infection.
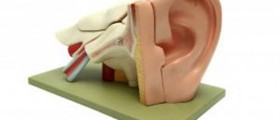
In toddlers the infection usually starts in upper respiratory tract and is then spread onto the ear. This is why initial symptoms of the infection include runny and snotty nose and sometimes runny and snotty eyes. The spread of the infection occurs due to connection between the throat and the middle area. They communicate via the Eustachian tube. Young children usually narrow Eustachian tubes. Infection of the upper respiratory tract causes swelling of the throat and consequent swelling of the Eustachian tube which narrows even more. Apart from swelling, the problem related to elimination of the excessive fluid from the middle ear is even more complicated by fact that this organ is placed more horizontal comparing to the Eustachian tube in adults. This interferes in proper draining of the fluid and leads to infection.
Symptoms of Ear Infection in Toddlers
In the beginning, the symptoms are related to infection of the upper respiratory tract and they include stuffy and runny nose. Apart from that, there is noticeable loss of appetite which may lead to weight loss. Loss of appetite is basically caused by pain and difficulty swallowing.
The pain in the ear occurs after certain period of time once the infection has spread onto the ear. The pain interferes in child's sleep, the child is irritated and cries all the time. He/ she may even hold the particular side of the head or ear which is affected by the infection. Excessive accumulation of the fluid inside the affected ear may cause hearing problems and the child may not respond to sounds. If the infection of the middle ear affects centers in charge with balance the child may have problems walking and loses balance. In rare cases the fluid from the ear may drain out. The color of the fluid is usually yellow-white.
Treatment for Ear Infection in Toddlers
Not all the children are prescribed antibiotics. In many cases ear infection may withdraw spontaneously. Administration of antibiotics in children may lead to undesirable effects and the child may vomit, develop diarrhea or skin rash. Up to 80 % of all ear infections in toddlers resolve within three days. The antibiotics are only administered if the symptoms last more than three days. The most commonly prescribed antibiotic is Amoxicillin. If there is no improvement after 48 hours of therapy the parents must take the child to pediatrician who will prescribe a new medication.



_f_280x120.jpg)









Your thoughts on this
Loading...