Dysarthria is defined as a motor speech disorder which develops as a consequence of injury to specific nerves. Person suffering from dysarthria has impaired articulatory abilities. So the problem in this condition is poor articulation and slurred speech. These people have lost the control over the muscles in charge with articulation such as muscles of the lips, throat, tongue or jaw muscles.
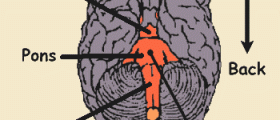
There are several types of dysarthria and they include spastic dysarthria, flaccid dysarthria, ataxic dysarthria, unilateral motor dysarthria and hyperkinetic/ hypokinetic dysarthria. Injury to the primary voluntary motor pathways typically leads to spastic dyarthria. In unilateral motor dysarthria the damage is located to the either side of the upper motor neuron tract. Damage to the cerebellum may result in ataxic dysarthria while flaccid dysarthria develops as a result of damage to the nerves of the brainstem and spinal cord. And finally, hyperkinetic dysarthria is associated with the damage to the upper part of the brainstem while hypokinetic dysarthria represents a consequence of damage to the basal ganglia.
Dysarthria - Causes and Symptoms
As it has already been mentioned damage to certain brain structures leads to specific type of dysarthria. The damage is basically caused by a variety of brain injuries, brain tumors, metabolic and degenerative illnesses and may occur after a stroke. Furthermore, this disorder may be one of the characteristics of Lyme disease, cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, Gullian- Barre syndrome, Parkinson's and Wilson's disease. In some cases dysarthria may be a side effect of certain narcotics and sedatives.
The condition typically features with slurred speech or slow rate of speech. The patient is simply not capable of controlling muscles in charge with speaking. Furthermore, there are changes in quality of the voice (nasal or stained voice) and in some cases patients can barely whisper. Apart from the previously mentioned patients suffering from dysarthria may additionally have problems with excess of saliva, chewing and swallowing difficulties.
Dysarthria- Treatment
Once the diagnosis of dysarthria is set the treatment basically depends on the type of dysarthria and the underlying cause. A patient usually undergoes many tests and examinations so that the exact cause of dysarthria can be identified. Some of these tests and examinations include CT scan, MRI, electroencephalogram, spinal tap, brain biopsy and a variety of blood tests.
Apart from treating the underlying cause the patients also undergo specific treatment which includes assistance of a speech language pathologist. He/she helps the patients by providing with a number of techniques and speech musculature exercises. If there is no improvement patients require alternative and augmentative alternative communication devices such as computerized speech synthesizers, alphabet board and in some cases they may communicate by gestures. These patients require additional help from physical and occupational therapists as well as neurophysiologists.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...