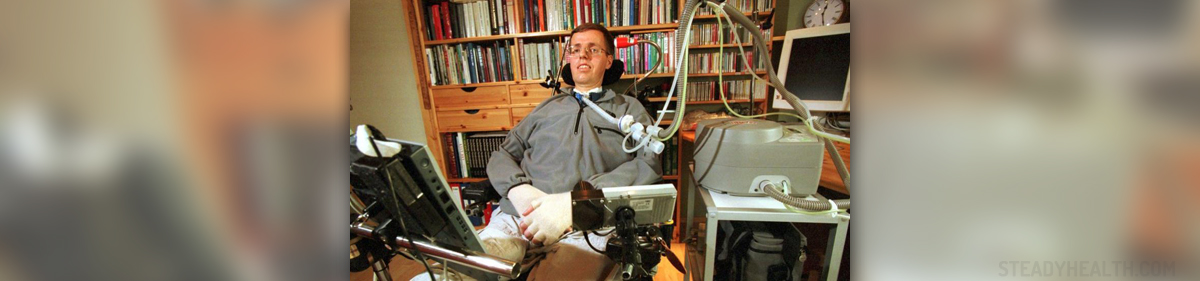
What Is Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis?
ALS, short for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, is a neurodegenerative disease which is characterized by the progressive degeneration of motor neurons. ALS typically leads to muscle weakness and consequent muscle atrophy. The damage is caused by degeneration of upper and lower motor neurons. In advanced stages of the disease, ALS patients are no longer capable of controlling their voluntary muscles. The bladder, bowel sphincter, as well as the muscles in charge of eye movement, may be spared. The disease eventually leads to problems in walking, talking, breathing, and performing most daily tasks.
Bulbar ALS may be only an introduction to ALS — the first sign of the disease. This form of ALS typically affects the tongue. Bulbar ALS is also known as bulbar onset of ALS.
Bulbar Onset of ALS: What is it?
In bulbar ALS, patients have problems with the tongue due to specific destruction of motor neurons. Patients suffering from bulbar ALS do not have to face problems with their limbs. In bulbar ALS, the disease primarily affects the facial nerves. These nerves originate from the medulla of the brain. Damage of motor neurons in this area causes specific symptoms of the disease. The progression of symptoms in bulbar ALS may eventually lead to spastic bulbar palsy. In bulbar ALS patients, apart from the tongue, the disease can also affect the throat, jaw and face in general. The bulbar form of the disease is reported to be the first stage of ALS in approximately 25 percent of all patients, and seeking medical attention early on can help a patient get started with treatment as soon as possible.
Symptoms and Signs of Bulbar ALS
The first symptom which affects people with bulbar ALS is slurred speech. Patients with bulbar ALS face difficulty when trying to pronounce certain words; the words become garbled and sometimes patients cannot even utter the words they were trying to communicate. Since the disease progresses in time, further symptoms that may emerge later include difficulty with swallowing and chewing.
In some patients, there is obvious problem with closing their eyes and mouth. One more symptom is drooling. Tremor and fasciculations of the tongue occur as well. The problem with the bulbar form of ALS is that symptoms and signs may progress much faster comparred to patients with limb onset of ALS.
There are serious complications related to bulbar ALS. The first one is potential choking caused by swallowing problems. Furthermore, these patients are susceptible to certain infections such as pneumonia. Breathing difficulties are most noticeable at night. Breathing difficulties consequently lead to headache, nocturnal dyspnea (shortness of breath at night), ortopnea (shortness of breath when lying down), nightmares, and sleepiness during the day.
The symptoms of bulbar ALS are initially very subtle and may, as such, be missed or dismissed. However, if a patient experiences any of the previously mentioned symptoms including spasticity and weakness while talking or chewing food or has strange feeling in the tongue, he or she is highly recommended to report this to their doctor right way. These symptoms do not, on their own, mean that a person is suffering from ALS. Bulbar ALS is only one of many possible causes of these symptoms, and medical attention should be sought to make it possible to identify the underlying cause of the problem and to treat potential illness on time.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...