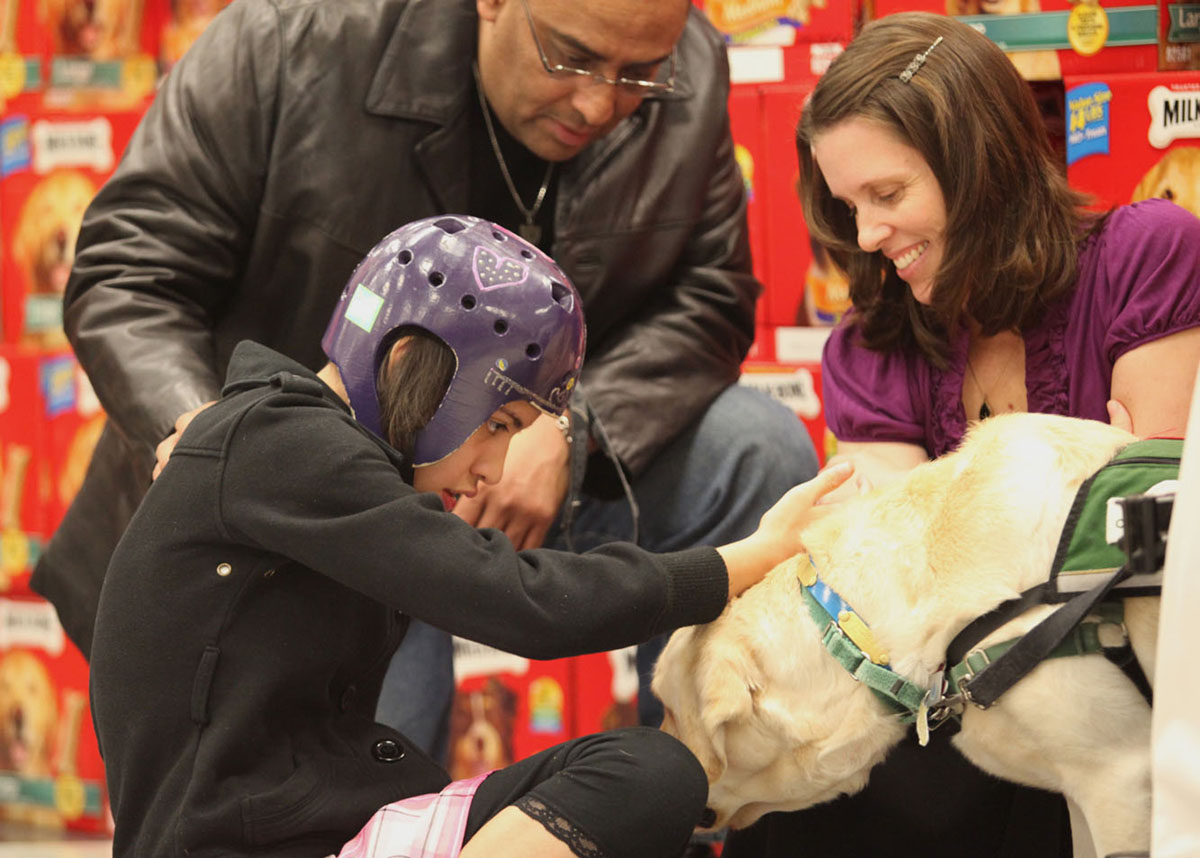

The only visible symptom of epilepsy is a seizure. A seizure is a sudden change in the behavior. Some seizures will make you fall, lose your consciousness, others you won’t even remember, or they might even remain unseen by others around you. Seizure can last differently, depending on a form of epilepsy you have.
Most of the seizures come unannounced, but it is possible to have an aura, almost like a prediction you’re going to seize.
Seizures happen in your brain, because of the sudden and temporary change in the electrical wiring of the brain, especially in the cortex of the brain.
According to the part of the brain in which the abnormality or change starts, epileptic seizures are divided into partial, where only some parts of the brain are involved, and generalized, where seizures take over the whole brain.
Partial epileptic seizures can be simple, complex or partial with secondary generalizations. Simple partial seizures are those that do not affect awareness and complex seizures will make you lose your consciousness. The third group of seizures starts as simple or complex, but then stretch to the complete brain.
Generalized seizures could be tonic-clonic seizures (sometimes called grand mal), which is how people usually think about an epileptic attack – the person falls onto the ground, starts shaking, muscles jerk, the persons then make sounds, drool, sometimes bite the tongue and sweat. Another form of general seizures is petit mal, or absence seizures. The person having this seizure may be just staring into blank space and doesn’t have to have visible spasms or even twitching of the eye. It could last for just a second to a minute and after the seizure, patient can’t recall that anything ever happened.
Other forms of generalized epilepsy are mioclonic seizures, when the whole body is shaking and atonic seizures, when a person suddenly lose the control over their muscles and just fall onto the ground and also tonic seizures. Atonic seizures are not damaging the brain, but the fall might have some serious consequences, if you fall and hit your head, for instance. In tonic seizures muscles contract unexpectedly and the person falls onto the ground.
There are then, special types of epilepsy: focal childhood epilepsy, childhood and juvenile absence epilepsy, infantile spasms (called West syndrome, present in newborns), juvenile myoclonic epilepsy, Lennox-Gastaut syndrome and temporal lobe epilepsy.
Epileptic attack is not a mental illness. Sometimes epilepsy in the children may severely compromise the intellect and cause problems in mental status and learning, but this happen only in most difficult cases.
A person having the epileptic attack is not crazy, violent, aggressive or dangerous.
Having a seizure doesn’t make you epileptic. Sometimes high fever, overuse of alcohol or drug, poisoning, another disease or injury could provoke the seizure, and once that condition is cured, the seizures stop too. If the seizures continue, they might become a chronic condition and a person could develop the epilepsy.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...