
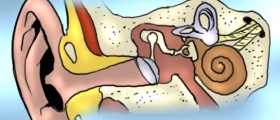
Deafness can be defined as the loss of hearing, which can occur due to many different reasons, most commonly a medical condition or a physical trauma. There can be several different classifications of types of deadness, depending on the point of view. Medically speaking, there are two main types: conductive deafness and sensorineural deafness.
In conductive deafness, the sound cannot pass through the middle or the outer ear, while in sensorineural deafness the cause lies in cochlea or in the auditory nerve.
Definitions associated with deafness
There are different terms that are used today to describe deafness. Some of them are synonymous but some have a slightly different meaning, depending on the type and cause of deafness.
When used with a lower case letter “d”, the word deaf is used simply to refer to a person who suffers from hear loss as a medical condition. However, in some sign languages, for example in British sign language, the word is spelled with a capital “D”, as Deaf, to describe a person that, politically, culturally and otherwise, belongs to the Deaf community. Deaf people usually do not refer to themselves as disabled, and they prefer thinking of themselves as of a cultural or a linguistic community.
“Hard of hearing” is a term used for persons who have hearing difficulties, which can range from minor problems to complete hear loss.
The term “hearing impaired” was considered to be the best politically correct solution, although today it seems to be abandoned.
Other terms
There are also other terms which can indicate the onset of deafness. Pre-lingually deaf indicates a person born without the ability to hear. Such person usually does not learn to communicate orally and uses sign language instead.
The term opposite to pre-lingually deaf is deafened. A deafened person was born with the ability to hear but he or she have lost that ability at some point in life, completely or partially.
Types of deafness
Conductive deafness, which is one type of this condition, is caused by the fact the sound is not conducted through the outer or middle ear.
In perceptive deafness, the sound reaches the inner ear, but it cannot be sensed because of a problem related to the nerves which lead to the brain.
There are other types of deafness as well. For example, deafness due to genetic or inherited factors, deafness due to exposure to noise, deafness caused by diseases such as meningitis, measles, mumps, otosclerosis, deafness caused by an injury to the ear and unilateral hearing loss, which only affects one ear.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...