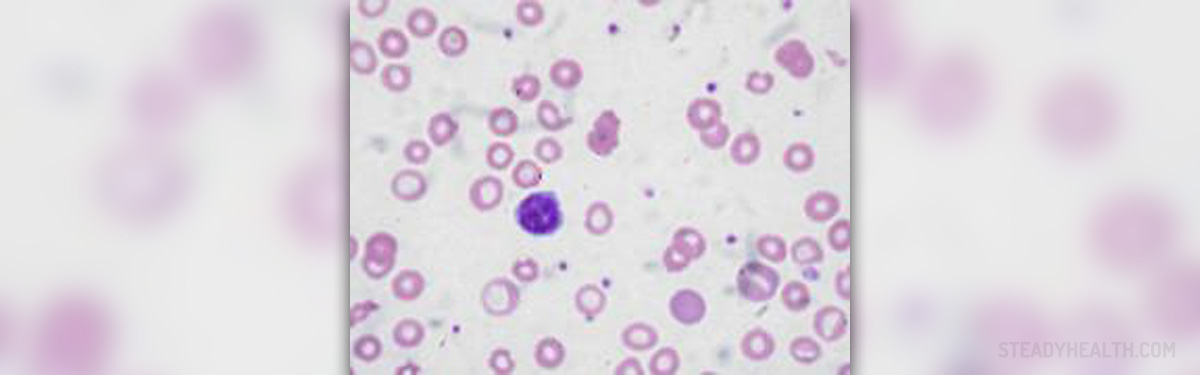
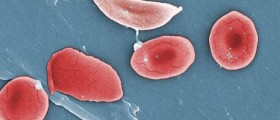
People who consume large amounts of phytates, dietary fiber, tannins and similar non-nutrient substances that inhibit absorption of iron as well as those who do not eat enough iron rich foods are at risk of developing iron deficiency anemia. This previously mentioned is the most common cause of anemia. Iron deficiency anemia is characterized by impaired production of red blood cells that supply tissues with oxygen. Iron is required by the body for hemoglobin production, a production of a red blood constituent that carries oxygen.
Causes of Iron Deficiency AnemiaIron deficiency anemia results from low blood iron levels. Impaired iron status can occur due to different reasons, but it most frequently develops because of dietary deficiencies. This includes low intake of iron-rich foods and lack of vitamin B12 (pernicious anemia) and folic acid.
The condition is more common in women and it may affect them during childbirth, pregnancy or during long and heavy menstrual periods. Iron deficiency anemia can result from regular use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), Aspirin or proton pump inhibitors.
Diseases and disorders like peptic ulcers, colon polyps, ulcerative colitis, colorectal cancer, a tumor of the kidney or bladder as well as uterine fibroids can also cause iron deficiency anemia. Intestinal disorders characterized by an inability to absorb iron such as Crohn’s disease or celiac disease can lead to iron deficiency anemia too.
Additionally, chronic diarrhea, parasitic infection and blood loss due to severe injuries can produce anemia.
Symptoms of Iron Deficiency Anemia
Any form of anemia causes fatigue, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, general malaise, pale skin (pallor) and cold hands/feet. Restless leg syndrome can also accompany anemia. Apart from these symptoms, iron deficiency anemia is associated with poor appetite, brittle nails, inflammation or soreness of the tongue and unusual cravings. The affected person may also suffer from decreased work capacity and physical endurance.
Complications of Iron Deficiency Anemia
Complications of iron deficiency anemia occur if the condition is left untreated. Iron deficiency anemia can cause serious complications such as heart problems. They include angina, tachycardia and heart failure.
In pregnancy, iron deficiency anemia increases the risk of many complications that may affect the mother, the baby or even both. It can cause preterm delivery, low birth weight, anemia in baby and postnatal depression.
Newborns with severe iron deficiency can suffer from delayed growth. This can eventually lead to physical and mental delays.
Due to uncorrected iron deficiency anemia, the person may have fragile and broken nails and experience hair loss. This form of anemia also increases susceptibility to infectious diseases.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...