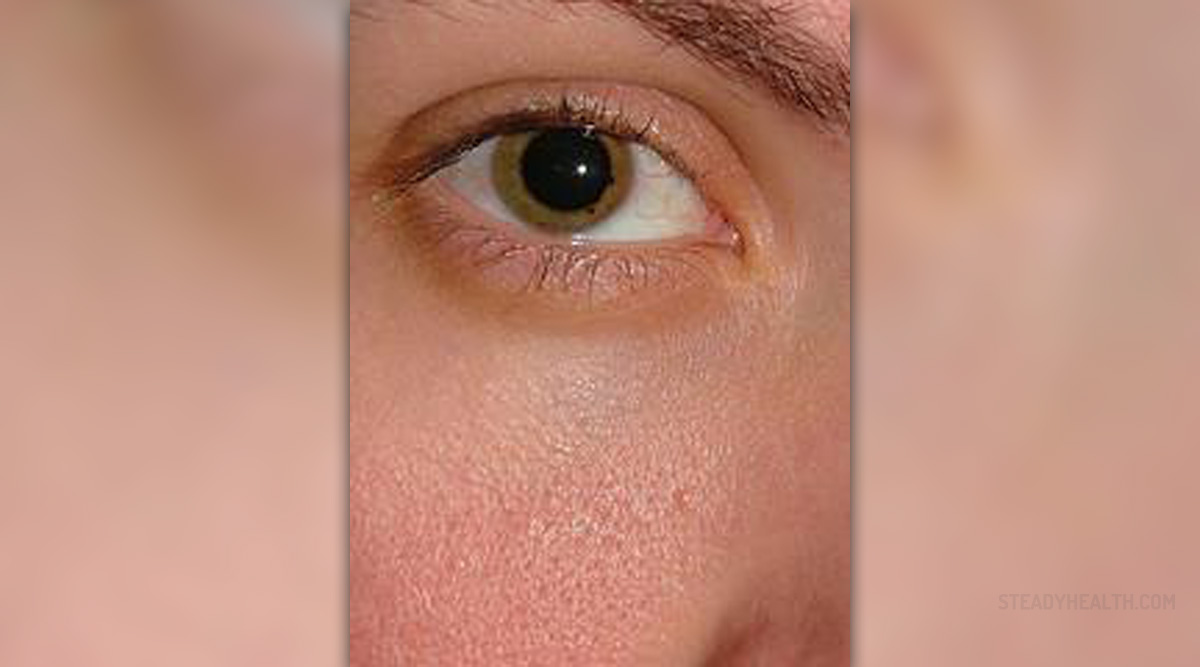
Diabetes is known to cause eye problems and because of that, patients are advised to regularly visit their ophthalmologist for some eye exams. High blood sugar increases the risk for eye problems in people suffering from diabetes and this is the most common cause of blindness in adult people, 20 to 74 years of age.
Blurred vision, cataract, glaucoma and retinopathy are problems of the eyes that may arise in diabetes patients. Sometimes, high blood sugar may temporarily worsen your vision and cause unclear sight. However, if this is the case, solution is to get your glucose level to normal and the vision will improve. Target range of blood sugar for people suffering from diabetes is about 90 to 130mg/dL before the meal or somewhere under 180mg/dL up to 2 hours after the meal.
Cataract in Diabetics
Clouding or fogging of the eye lenses is known as cataract, which causes inability to focus light and impaired (blurred and glared) vision. This condition is not something happening only to diabetics, but these patients are more likely to develop it at earlier age comparing to any other group of people. Also, if someone already has diabetes and develops cataract, the problem will become worse than usual in a short period of time. Surgical treatment and lens implants are usual methods of treatment and many patients require further wearing of glasses or contact lenses.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetes might also affect blood vessels and cause microvascular problems, such as retinopathy, kidney disease and some nerve damage. High blood sugar must be kept under control if the patient wants to prevent irreversible damage to his/her organs, including permanent damage to the eye.
Diabetic neuropathy has been known to be the leading cause of permanent blindness in modern world. This condition must be diagnosed in time and treated in order to avoid such consequences. Duration of diabetes determines the risk of developing diabetic neuropathy, so patients suffering from type 1 diabetes may develop this condition even before puberty. There are several types of this condition, including background retinopathy, maculopathy and proliferative retinopathy.Preventive Measures
To prevent eye problems related to diabetes, patients suffering from this disease should regularly control their blood sugar and keep it within recommended range. Type 1 diabetes patients should check their eyes 3 to 5 years after the diagnosis, and those with type 2 diabetes should perform dilated eye exam soon after they find out they are having diabetes.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...